Page 12 - JCTR-11-5
P. 12
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research AI and LLMs in iPSC cardiac research
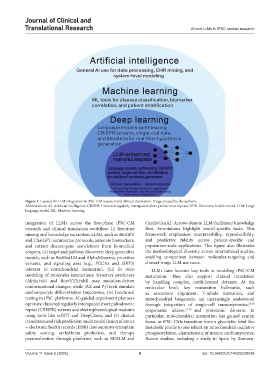
Figure 1. Layered AI-LLM integration in iPSC-CM research and clinical translation. Image created by the authors.
Abbreviations: AI: Artificial intelligence; CRISPR: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; EHR: Electronic health record; LLM: Large
language model; ML: Machine learning.
integration of LLMs across the five-phase iPSC-CM CardioGenAI. Arrows denote LLM-facilitated knowledge
research and clinical translation workflow: (i) literature flow. Annotations highlight model-specific tasks. This
mining and knowledge extraction: LLMs, such as BioGPT framework emphasizes interpretability, reproducibility,
and ChatGPT, summarize protocols, annotate biomarkers, and predictive fidelity across patient-specific and
and extract disease-gene associations from biomedical population-scale applications. This figure also illustrates
corpora, (ii) target and pathway discovery: deep generative the methodological diversity across international studies,
models, such as BioMedLM and AlphaMissense, prioritize enabling comparison between molecular-targeting and
variants, and signaling axes (e.g., PGC1α and SIRT3) clinical-triage LLM use cases.
relevant to mitochondrial maturation, (iii) In silico LLMs have become key tools in modeling iPSC-CM
modeling of molecular interactions: Structure predictors maturation. They also support clinical translation
(AlphaFold and RoseTTAFold) map mutation-driven by handling complex, multi-layered datasets. At the
conformational changes, while JAX and PyTorch simulate molecular level, key maturation hallmarks, such
cardiomyocyte differentiation trajectories, (iv) functional as sarcomere alignment, T-tubule formation, and
testing in iPSC platforms: AI-guided experiment planners mitochondrial biogenesis, are increasingly understood
optimize clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic through integration of single-cell transcriptomics, 29,30
repeat (CRISPR) screens and electrophysiological readouts epigenomic atlases, 31-35 and proteomic datasets. In
using tools like scGPT and DeepChem, and (v) clinical particular, mitochondrial maturation has gained central
translation and risk prediction: multimodal fusion of omics focus, as iPSC-CMs transition from a glycolytic, fetal-like
+ electronic health records (EHR) data supports transplant metabolic profile to one reliant on mitochondrial oxidative
safety scoring, arrhythmia prediction, and therapy phosphorylation, characteristic of mature cardiomyocytes.
personalization through platforms, such as REALM and Recent studies, including a study in Spain by Zamora-
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025230026