Page 14 - JCTR-11-5
P. 14
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research AI and LLMs in iPSC cardiac research
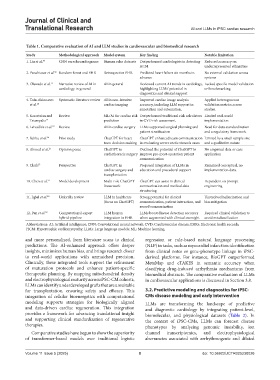
Table 1. Comparative evaluation of AI and LLM studies in cardiovascular and biomedical research
Study Methodological approach Model system Key finding Notable limitation
1. Liu et al. 37 CNN on echocardiograms Human echo datasets Outperformed cardiologists in detecting Reduced accuracy on
HCM underrepresented ethnicities
2. Panahiazar et al. 38 Random forest and EHR Retrospective EHR Predicted heart failure six months in No external validation across
advance systems
3. Olawade et al. 15 Narrative review of AI in AI in general Reviewed current AI trends in cardiology, Lacked specific model validation
cardiology in general highlighting LLMs’ potential in or benchmarking
diagnostics and clinical support
4. Tolu-Akinnawo Systematic literature review AI in non-invasive Improved cardiac image analysis Applied heterogeneous
et al. 16 cardiac imaging accuracy, including LLM support in validation metrics across
annotation and automation. studies.
5. Kasartzian and Review ML/AI for cardiac risk Outperformed traditional risk calculators Limited real-world
Tsiampalis 17 prediction in CVD risk assessment. implementation
6. Leivaditis et al. 18 Review AI in cardiac surgery LLMs supported surgical planning and Need for data standardization
patient stratification and a regulatory framework
7. Salihu et al. 24 Pilot study ChatGPT for heart ChatGPT enhanced team communication Limited by a small sample size
team decision making in evaluating severe arctic stenosis cases and a qualitative nature
8. Ahmed et al. 25 Opinion peace ChatGPT in Outlined the potential of ChatGPT to No empirical data or case
cardiothoracic surgery improve pre-/post-operation patient application
communication
9. Clark 27 Perspective ChatGPT in Proposed integration of LLMs in Remained conceptual, no
cardiac surgery and education and procedural support implementation data.
transplantation
10. Chen et al. 21 Model development Multi-role ChatGPT ChatGPT can assist in clinical Dependent on prompt
framework summarization and medical data engineering
structuring
11. Iqbal et al. 20 Umbrella review LLM in healthcare Strong potential for clinical Unresolved hallucination and
(focus on ChatGPT) communication, patient interaction, and bias mitigation
record summarization
12. Pan et al. 39 Computational-expert LLM human LLMs boost disease detection accuracy Required clinical validation to
hybrid pipeline integration in EHR when augmented with clinical oversight avoid misclassification
Abbreviations: AI: Artificial intelligence; CNN: Convolutional neural network; CVD: Cardiovascular disease; EHRs: Electronic health records;
HCM: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; LLMs: Large language models; ML: Machine learning.
and more personalized, from literature scans to clinical regression or rule-based natural language processing
predictions. The AI-enhanced approach offers deeper (NLP) in tasks, such as myocardial infarction identification
insights, minimizes human bias, and brings research closer from clinical notes or gene-phenotype linkage in iPSC-
to real-world applications with unmatched precision. derived platforms. For instance, BioGPT outperformed
Clinically, these integrated tools support the refinement MetaMap and cTAKES in semantic accuracy when
of maturation protocols and enhance patient-specific classifying drug-induced arrhythmia mechanisms from
therapeutic planning. By mapping mitochondrial density biomedical abstracts. The comparative evaluation of LLMs
and electrophysiological maturity across iPSC-CM cohorts, in cardiovascular applications is discussed in Section 3.8.
LLMs can identify underdeveloped grafts that are unsuitable
for transplantation, ensuring safety and efficacy. This 3.2. Predictive modeling and diagnostics for iPSC-
integration of cellular bioenergetics with computational CMs disease modeling and early intervention
modeling supports strategies for biologically aligned LLMs are transforming the landscape of predictive
and data-driven cardiac regeneration. This integration and diagnostic cardiology by integrating patient-level,
provides a framework for advancing translational insight biomolecular, and physiological datasets (Table 2). In
and supporting clinical standardization of regenerative the context of iPSC-CMs, LLMs can forecast disease
therapies. phenotypes by analyzing genomic instability, ion
Comparative studies have begun to show the superiority channel transcriptomics, and electrophysiological
of transformer-based models over traditional logistic aberrancies associated with arrhythmogenic and dilated
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025230026