Page 15 - JCTR-11-5
P. 15
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research AI and LLMs in iPSC cardiac research
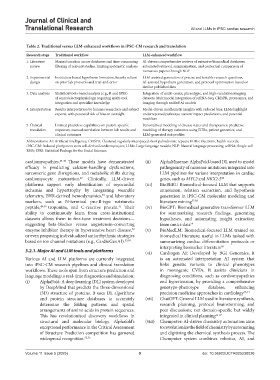
Table 2. Traditional versus LLM‑enhanced workflows in iPSC‑CM research and translation
Research stage Traditional workflow LLM‑enhanced workflow
1. Literature Manual curation across databases and time-consuming AI-driven comprehensive reviews of extensive biomedical databases;
review filtering of relevant studies, limiting systematic analysis automated retrieval, summarization, and contextual comparison of
numerous papers through NLP
2. Experimental Institution-based hypothesis formation, heavily reliant LLM-assisted generation of precise and testable research questions,
design on prior lab protocols and trial-and-error AI-assisted hypothesis generation, and protocol optimization based on
similar published data
3. Data analysis Statistical tools-based analysis (e.g., R and SPSS) Integration of multi-omics, phenotypic, and high-resolution imaging
of omics/electrophysiology, requiring multi-tool datasets. Multimodal integration of scRNA-Seq, CRISPR, proteomics, and
integration and specialist knowledge imaging through unified AI models
4. Interpretation Results interpretation by human researchers and subject Model-driven mechanistic insights with reduced bias; LLMs highlight
experts, with potential risk of bias or oversight underreported pathways, variant impact predictions, and potential
modifiers
5. Clinical Limited predictive capabilities on patient-specific Personalized modeling of disease states and therapeutics; predictive
translation responses, manual correlation between lab results and modeling of therapy outcomes using EHRs, patient genomics, and
clinical outcomes LLM-generated risk profiles
Abbreviations: AI: Artificial intelligence; CRISPR: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; EHRs: Electronic health records;
iPSC-CM: Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes; LLMs: Large language models; NLP: Natural language processing; scRNA: Single-cell
RNA; SPSS: Statistical Package for the Social Sciences.
cardiomyopathies. 44-46 These models have demonstrated (ii) AlphaMissense: AlphaFold-based DL used to model
efficacy in predicting calcium-handling dysfunctions, pathogenicity of missense mutations; integrated into
sarcomeric gene disruptions, and metabolic shifts during LLM pipelines for variant interpretation in cardiac
cardiomyocyte maturation. Clinically, LLM-driven genes, such as MYL2 and NKX2-5 44
47
platforms support early identification of myocardial (iii) BioBERT: Biomedical-focused LLM that supports
ischemia and hypertrophy by integrating wearable annotation, relation extraction, and hypothesis
48
telemetry, EHR-derived hemodynamics, and laboratory generation in iPSC-CM molecular modeling and
markers, such as N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic literature mining 57,58
peptide, 49,50 troponins, and C-reactive protein. Their (iv) BioGPT: Biomedical generative transformer LLM
51
ability to continuously learn from cross-institutional for summarizing research findings, generating
datasets allows them to fine-tune treatment decisions— hypotheses, and automating insight extraction
suggesting beta-blocker versus angiotensin-converting from omics data 59
enzyme inhibitor therapy in hypertensive heart disease, (v) BioMedLM: Biomedical-focused LLM trained on
52
or even proposing individualized antiarrhythmic strategies biomedical literature; useful in LLMs tasked with
based on ion channel mutations (e.g., CardioGenAI). 53,54 summarizing cardiac differentiation protocols or
interpreting biomarker literature 60
3.2.1. Major AI and LLM tools and platforms (vi) Cardiogen AI: Developed by BGI Genomics, it
Various AI and LLM platforms are currently integrated is an automated interpretation AI system that
into iPSC-CM research pipelines and clinical translation links genetic variants to clinical phenotypes
workflows. These tools span from structure prediction and in monogenic CVDs. It assists clinicians in
language modeling to real-time diagnostics and simulation: diagnosing conditions, such as cardiomyopathies
(i) AlphaFold: A deep learning (DL) system developed and hypertension, by providing a comprehensive
by DeepMind that predicts the three-dimensional genotype-phenotype database, enhancing
(3D) structure of proteins. It uses DL algorithms precision medicine approaches in cardiology 53,54
and protein structure databases to accurately (vii) ChatGPT: General LLM used in literature synthesis,
determine the folding patterns and spatial research planning, protocol brainstorming, and
arrangements of amino acids in protein sequences. peer discussions; not domain-specific but widely
This has revolutionized discovery workflows in integrated in clinical planning 21-27
structural and molecular biology. Alphafold’s (viii) Chemputer: AI-driven chemistry automation aims
exceptional performance in the Critical Assessment to revolutionize the field of chemistry by automating
of Structure Prediction competition has garnered and digitizing the chemical synthesis process. The
widespread recognition. 55,56 Chemputer system combines robotics, AI, and
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 9 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025230026