Page 8 - JCTR-9-5
P. 8
310 Songtanin et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(5): 308-316
between appendectomy and colorectal cancer in each study group.
These studies did not report the indication for appendectomy or
the histology of the resected appendices.
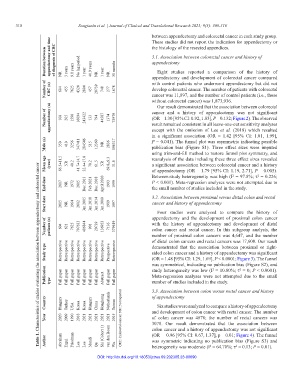
Duration between appendectomy and time of diagnosis of CRC NR 3 years 9.8 years No lag period 1 year 40.9 years NR 1 year NR 30 months 3.1. Association between colorectal cancer and history of
appendectomy
Eight studies reported a comparison of the history of
Number of CRC (n) 604 455 7625 4324 2804 457 20739 748 277 1678 appendectomy and development of colorectal cancer compared
with control patients who underwent appendectomy but did not
develop colorectal cancer. The number of patients with colorectal
cancer was 11,897, and the number of control patients (i.e., those
without colorectal cancer) was 1,873,936.
Our result demonstrated that the association between colorectal
Number of appendectomy (n) 100 205 1590 16094 243422 133 794 44587 1374 75979 cancer and a history of appendectomy was not significant
(OR = 1.30 [95% CI: 0.92, 1.83], P = 0.132; Figure 2). The observed
result remained consistent in all leave-one-out sensitivity analyses
except with the omission of Lee et al. (2018) which resulted
in a significant association (OR = 1.42 [95% CI: 1.01, 1.99],
Male (n) 350 410 3256 347411 284546 515 12360 NR 2836 196317 P = 0.041). The funnel plot was asymmetric indicating possible
publication bias (Figure S1). Three effect sizes were imputed
using trim-and-fill method to restore funnel plot symmetry, and
Mean age (year) 66.5±11.5 NR 40.2 41.7±14.7 32.4±17.0 70.2 61.5 NR 69.8±9.3 31.8 reanalysis of the data including these three effect sizes revealed
a significant association between colorectal cancer and a history
Table 1. Characteristics of studies evaluating the association between appendectomy and colorectal cancer
of appendectomy (OR = 1.79 [95% CI: 1.19, 2.71], P = 0.005).
2
2
End date 2017 NR 1972 2015 Dec 2013 Feb 2021 Dec 2018 April 2020 1993 1999 Between-study heterogeneity was high (I = 97.8%; τ = 0.226;
P < 0.001). Meta-regression analyses were not attempted due to
the small number of studies included in the study.
Start date 2015 NR 1964 2002 Jan 2005 Jan 2018 Jan 2014 Jan 2000 1989 1997 3.2. Association between proximal versus distal colon and rectal
cancer and history of appendectomy
Four studies were analyzed to compare the history of
Number of patients (n) 604 621 7625 707633 486844 901 20739 136953 7136 379619 appendectomy and the development of proximal colon cancer
with the history of appendectomy and development of distal
colon cancer and rectal cancer. In this subgroup analysis, the
number of proximal colon cancers was 4,647, and the number
Study type Retrospective Retrospective Retrospective Retrospective Retrospective Retrospective Retrospective Retrospective Prospective Retrospective of distal colon cancers and rectal cancers was 17,608. Our result
demonstrated that the association between proximal or right-
sided colon cancer and a history of appendectomy was significant
(OR = 1.48 [95% CI: 1.29, 1.69], P < 0.0001; Figure 3). The funnel
was symmetrical, indicating no publication bias (Figure S2), and
Publication type Full paper Full paper Full paper Full paper Full paper Full paper Full paper Abstract Full paper Full paper study heterogeneity was low (I = 10.80%; τ = 0; P < 0.0001).
2
2
Meta-regression analyses were not attempted due to the small
number of studies included in the study.
of appendectomy
Country Hungary Turkey USA Korea Korea Hungary China Hongkong Netherlands Taiwan 3.3. Association between colon versus rectal cancer and history
Six studies were analyzed to compare a history of appendectomy
Year 2020 2009 1990 2018 2021 2021 2021 2021 2021 2015 CRC: Colorectal cancer; NR: Not reported and development of colon cancer with rectal cancer. The number
of colon cancer was 4676; the number of rectal cancers was
3078. Our result demonstrated that the association between
colon cancer and a history of appendectomy was not significant
Author Abraham Ergul Friedman Lee Lee Mandi Qu Shi (Cohort 1) van den Boom Wu (OR = 0.96 [95% CI: 0.67, 1.37], p = 0.01; Figure 4). The funnel
was symmetric indicating no publication bias (Figure S3) and
heterogeneity was moderate (I = 64.70%; τ = 0.13; P = 0.01).
2
2
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202305.23-00090