Page 37 - MI-1-2
P. 37
Microbes & Immunity Host receptors in immunogenic cell death
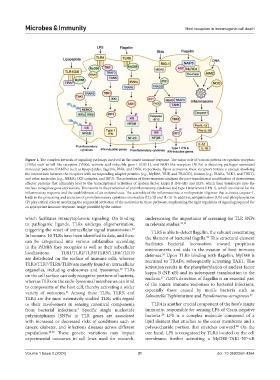
Figure 1. The complex network of signaling pathways involved in the innate immune response. The major role of various pattern recognition receptors
(PRRs) such as toll-like receptors (TLRs), retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-1), and NOD-like receptors (NLRs) is detecting pathogen-associated
molecular patterns (PAMPs) such as lipopeptides, flagellin, RNA, and DNA, respectively. Upon activation, these receptors initiate a cascade involving
the interactions between the receptors with corresponding adaptor proteins (e.g., MyD88, TRIF, and TRADD), kinases (e.g., IRAKs, TAK1, and TBK1),
and other molecules (e.g., NEMO, IKK complex, and IRF3). The activation of these enzymes catalyzes the post-translational modification of downstream
effector proteins that ultimately lead to the transcriptional activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and IRF3, which then translocate into the
nucleus to regulate gene expressions. This results in the production of proinflammatory cytokines and type I interferons (IFN-I), which are crucial for the
inflammatory response and the establishment of an antiviral state. The assembly of the inflammasome, a multiprotein oligomer that activates caspase-1,
leads to the processing and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18. In addition, ubiquitination (Ub) and phosphorylation
(P) play critical roles in mediating the sequential activation of the molecules in these pathways, emphasizing the tight regulation of signaling required for
an appropriate immune response. Image provided by the author.
which facilitates intracytoplasmic signaling. On binding underscoring the importance of screening for TLR SNPs
to pathogenic ligands, TLRs undergo oligomerization, in relevant studies. 23,24
triggering the onset of intracellular signal transmission. TLR5 is able to detect flagellin, the subunit constituting
20
In humans, 10 TLRs have been identified to date, and these the filament of bacterial flagella. This structural element
25
can be categorized into various subfamilies according facilitates bacterial locomotion toward propitious
to the PAMPs they recognize as well as their subcellular environments and aids in the evasion of host immune
localizations. TLR1/TLR2/TLR4/TLR5/TLR6/TLR10 defenses. Upon TLR5 binding with flagellin, MyD88 is
26
are distributed on the surface of immune cells, whereas recruited to TRAF6, subsequently activating TAK1. This
TLR3/TLR7/TLR8/TLR9 are mostly found on intracellular activation results in the phosphorylation of nuclear factor
organelles, including endosomes and lysosomes. TLRs kappa B (NF-κB) and its subsequent translocation to the
20
on the cell surface can only recognize portions of bacteria, nucleus. TLR5’s detection of flagellin is an essential part
27
whereas TLRs on the endo-lysosomal membranes can bind of the innate immune responses to bacterial infections,
to components of the host cell, thereby activating a wider
21
variety of outcomes. Among these TLRs, TLR5, and especially those caused by motile bacteria such as
27
TLR4 are the most extensively studied TLRs with regard Salmonella Typhimurium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
to their involvement in sensing canonical components TLR4 is another crucial component of the host’s innate
from bacterial infections. Specific single nucleotide immunity, responsible for sensing LPS of Gram-negative
3
polymorphisms (SNPs) in TLR genes are associated bacteria. LPS is a complex molecule composed of a
28
with increased or decreased risks of conditions such as lipid element that attaches to the outer membrane and a
28
cancer, diabetes, and infectious diseases across different polysaccharide portion that stretches outward. On the
populations. 22,23 These genetic variations may impact one hand, LPS is recognized by TLR4 located on the cell
experimental outcomes in cell lines used for research, membrane, further activating a MyD88-TAK1-NF-κB
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 31 doi: 10.36922/mi.4264