Page 81 - MI-1-2
P. 81
Microbes & Immunity Hydrogen alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
A B C F
D E
G H I
J K L M
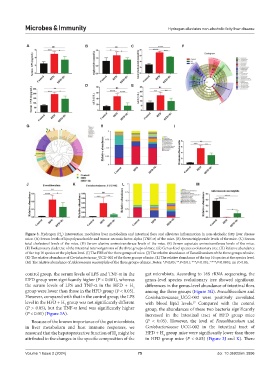
Figure 3. Hydrogen (H ) intervention modulates liver metabolism and intestinal flora and alleviates inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
2
mice. (A) Serum levels of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) of the mice. (B) Serum triglyceride levels of the mice. (C) Serum
total cholesterol levels of the mice. (D) Serum alanine aminotransferase levels of the mice. (E) Serum aspartate aminotransferase levels of the mice.
(F) Evolutionary clade tree of the intestinal microorganisms of the three groups of mice. (G) Genus-level species evolutionary tree. (H) Relative abundance
of the top 10 species at the phylum level. (I) The FBR of the three groups of mice. (J) The relative abundance of Faecalibaculum of the three groups of mice.
(K) The relative abundance of Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002 of the three groups of mice. (L) The relative abundance of the top 10 species at the species level.
(M) The relative abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila of the three groups of mice. Notes: *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001; ns: P>0.05.
control group, the serum levels of LPS and TNF-α in the gut microbiota. According to 16S rRNA sequencing, the
HFD group were significantly higher (P < 0.001), whereas genus-level species evolutionary tree showed significant
the serum levels of LPS and TNF-α in the HFD + H differences in the genus-level abundance of intestinal flora
2
group were lower than those in the HFD group (P < 0.05). among the three groups (Figure 3G). Faecalibaculum and
However, compared with that in the control group, the LPS Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002 were positively correlated
level in the HFD + H group was not significantly different with blood lipid levels. Compared with the control
17
2
(P > 0.05), but the TNF-α level was significantly higher group, the abundances of these two bacteria significantly
(P < 0.01) (Figure 3A). increased in the intestinal tract of HFD group mice
Because of the known importance of the gut microbiota (P < 0.05). However, the level of Faecalibaculum and
in liver metabolism and host immune responses, we Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002 in the intestinal tract of
reasoned that the hepatoprotective function of H might be HFD + H group mice were significantly lower than those
2
2
attributed to the changes in the specific composition of the in HFD group mice (P < 0.05) (Figure 3J and K). There
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 75 doi: 10.36922/mi.3896