Page 72 - MI-2-1
P. 72
Microbes & Immunity Copper and cuproptosis in immunity
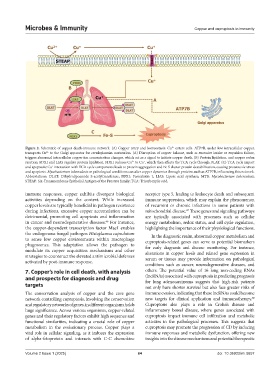
Figure 2. Schematic of copper death-immune network. (A) Copper entry and homeostasis: Cu enters cells. ATP7B, under low intracellular copper,
2+
transports Cu to the Golgi apparatus for ceruloplasmin maturation. (A) Disruption of copper balance, such as excessive intake or expulsion failure,
2+
triggers abnormal intracellular copper ion concentration changes, which act as a signal to initiate copper death. (B) Protein lipidation, and copper redox
reaction: FDX1 and LIAS regulate protein lipidation. FDX1 reduces Cu to Cu , which then affects the TCA cycle through DLAT. (C) TCA cycle impact
2+
+
and apoptosis: Cu interaction with TCA cycle components leads to protein aggregation and Fe-S cluster protein destabilization, causing proteotoxic stress
+
and apoptosis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis or pathological conditions can alter copper dynamics through proteins such as ATP7B, influencing this network.
Abbreviations: DLAT: Dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase; FDX1: Ferredoxin 1; LIAS: Lipoic acid synthase; MTB: Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
STEAP: Six-Transmembrane Epithelial Antigen of the Prostate family; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid.
immune responses, copper exhibits divergent biological receptor type 5, leading to leukocyte death and subsequent
activities depending on the context. While increased immune suppression, which may explain the phenomenon
copper levels are typically beneficial in pathogen resistance of recurrent or chronic infections in some patients with
during infections, excessive copper accumulation can be mitochondrial disease. These genes and signaling pathways
67
detrimental, promoting cell apoptosis and inflammation are typically associated with processes such as cellular
66
in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. For instance, energy metabolism, redox status, and cell cycle regulation,
the copper-dependent transcription factor Mac1 enables highlighting the importance of their physiological functions.
the endogenous fungal pathogen Histoplasma capsulatum In the diagnostic realm, abnormal copper metabolism and
to sense low copper environments within macrophage cuproptosis-related genes can serve as potential biomarkers
phagosomes. This adaptation allows the pathogen to for early diagnosis and disease monitoring. For instance,
modulate its copper acquisition mechanisms and other alterations in copper levels and related gene expression in
strategies to counteract the elevated antimicrobial defenses serum or tissues may provide information on pathological
activated by post-immune response.
conditions such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and
7. Copper’s role in cell death, with analysis others. The potential value of 16 long non-coding RNAs
and prospects for diagnosis and drug (lncRNAs) associated with cuproptosis in predicting prognosis
for lung adenocarcinoma suggests that high-risk patients
targets not only have shorter survival but also face greater risks of
The conservation analysis of copper and the core gene immune evasion, indicating that these lncRNAs could become
network controlling cuproptosis, involving the conservation new targets for clinical application and immunotherapy.
68
and regulatory networks of genes, in different organisms holds Cuproptosis also plays a role in Crohn’s disease and
huge significance. Across various organisms, copper-related inflammatory bowel disease, where genes associated with
genes and their regulatory factors exhibit high sequence and cuproptosis impact immune cell infiltration and metabolic
functional similarities, indicating a crucial role of copper activities in the pathological processes. This suggests that
metabolism in the evolutionary process. Copper plays a cuproptosis may promote the progression of CD by inducing
vital role in cellular signaling, as it induces the expression immune responses and metabolic dysfunction, offering new
of alpha-fetoprotein and interacts with C-C chemokine insights into the disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 64 doi: 10.36922/mi.5657