Page 102 - MI-2-3
P. 102
Microbes & Immunity SARS-CoV-2 complementary classification
year of 2074 (range: 2046 – 2148). The median estimate corresponding to a projected divergence year of 2147
was 43.8 years, or the year 2064, with a right-skewed (range: 2082 – 2324), with a median of 103.5 years (year
distribution reflecting variability in substitution rates. 2124). For the influenza A virus threshold (1.956 s/s),
For HCV-level divergence (0.371 s/s), the mean estimated the mean estimated time to comparable divergence
timeframe was 126.8 years (95% CI: 123.0 – 130.6), was 668.6 years (95% CI: 648.4 – 688.7), translating to a
projected year of 2689 (range: 2346 – 3620), with a median
Table 1. Estimates of evolutionary divergence over sequence of 545.7 years, or the year 2566 (Figure 6).
pairs between HIV‑1 subtypes/CRFs
3.7. Application of the new literature-based
HIV‑1 species 1 HIV‑1 species 2 Genetic distance (s/s) classification system to existing SARS-CoV-2 variants
CRF01_AE C 0.231
CRF02_AG CRF01_AE 0.200 To evaluate whether existing SARS-CoV-2 variants met the
criteria for variant classification, each was assessed using
CRF02_AG C 0.227 the new literature-based classification system as follows:
A CRF02_AG 0.157 (1) Genetic distance analysis: None of the examined
A CRF01_AE 0.203 SARS-CoV-2 variants exceeded the moderate divergence
A C 0.223 threshold (0.157 s/s); (2) Functional and epidemiological
B D 0.188 review: While some variants demonstrated increased
B A 0.220 transmissibility and immune escape, none met all
B CRF02_AG 0.223 classification functional criteria. Omicron sub-lineages
B CRF01_AE 0.226 exhibited notable immune evasion but did not substantially
increase clinical severity or hospitalization rates
B C 0.227 beyond prior VOCs; and (3) Longitudinal surveillance:
D A 0.219 No SARS-CoV-2 variant maintained dominance for
D CRF02_AG 0.230 >12 months or necessitated a fundamental vaccine update,
D CRF01_AE 0.235 which would indicate a stable antigenic drift pattern.
D C 0.229 These findings suggest that the present classification of
Abbreviations: CRFs: Circulating recombinant forms; HIV-1: Human SARS-CoV-2 variants as distinct lineages is not supported
immunodeficiency virus 1; s/s: Substitutions per site. by genetic, virological, or epidemiological data. Under
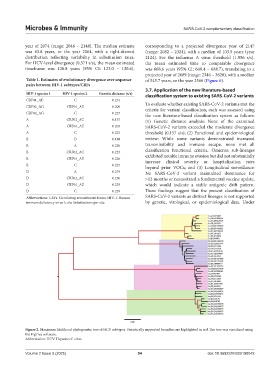
Figure 2. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of HCV subtypes. Statistically supported branches are highlighted in red. The tree was visualized using
the FigTree software.
Abbreviation: HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 94 doi: 10.36922/MI025190042