Page 155 - MI-2-3
P. 155
Microbes & Immunity Hyphae and healthspan
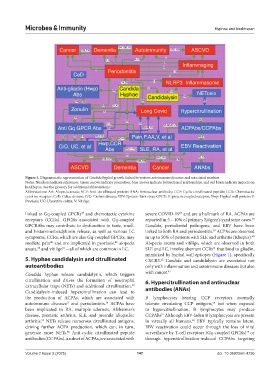
Figure 1. Diagrammatic representation of Candida hyphal growth linked to various autoimmune diseases and associated markers
Notes: Numbers indicate references. Green arrows indicate promotion, blue arrows indicate bidirectional relationships, and red boxes indicate impacts on
healthspan. See the glossary for additional abbreviations.
Abbreviations: AA: Alopecia areata; ACP: Anti-citrullinated protein; ANA: Antinuclear antibody; CCP: Cyclic citrullinated peptide; CCR: Chemotactic
cytokine receptor; CeD: Celiac disease; CrD: Crohn’s disease; EBV: Epstein–Barr virus; GPCR: G-protein coupled receptor; Hwp: Hyphal wall protein; P:
Psoriasis; UC: Ulcerative colitis; V: Vitiligo.
linked to Gq-coupled GPCRs and chemotactic cytokine severe COVID-19 and are a hallmark of RA. ACPAs are
35
57
receptors (CCRs). GPCRs associated with Gq-coupled reported in 5 – 10% of primary Sjögren’s syndrome cases.
58
GPCRAbs may contribute to dysfunction in taste, smell, Candida, periodontal pathogens, and EBV have been
and histamine/bradykinin release, as well as various LC linked to both RA and periodontitis. ACPAs are observed
59
symptoms. CCRs, which are also Gq-coupled GPCRs, may in up to 50% of patients with SLE and arthritis (Rhupus).
60
mediate pain and are implicated in psoriasis, alopecia Alopecia areata and vitiligo, which are observed in both
49
48
areata, and vitiligo —all of which are common in LC. SLE and LC, involve aberrant CCRs that bind to gliadin,
51
61
50
mimicked by hyphal wall epitopes (Figure 1), specifically
5. Hyphae candidalysin and citrullinated CXCR3. Candida and candidalysin are associated not
62
autoantibodies only with inflammation and autoimmune diseases but also
Candida hyphae release candidalysin, which triggers with cancer. 63
citrullination and drives the formation of neutrophil 6. Hypercitrullination and antinuclear
extracellular traps (NETs) and additional citrullination.
52
Candidalysin-induced hypercitrullination can lead to antibodies (ANAs)
the production of ACPAs, which are associated with B lymphocytes bearing CCP receptors normally
autoimmune diseases and periodontitis. ACPAs have tolerate circulating CCP antigens, but when exposed
54
53
64
been implicated in RA, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s to hypercitrullination, B lymphocytes may produce
disease, psoriatic arthritis, SLE, and juvenile idiopathic CCPAbs Although EBV-laden B lymphocytes are present
53
65
arthritis. NETs release numerous citrullinated antigens, in virtually all humans, EBV typically remains latent.
55
driving further ACPA production, which can, in turn, EBV reactivation could occur through the loss of viral
35
generate more NETs. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide surveillance by T-cell receptors (Gq-coupled GPCRs) or
56
antibodies (CCPAbs), a subset of ACPAs, are associated with through hypercitrullination-induced CCPAbs targeting
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 147 doi: 10.36922/mi.4736