Page 157 - MI-2-3
P. 157
Microbes & Immunity Hyphae and healthspan
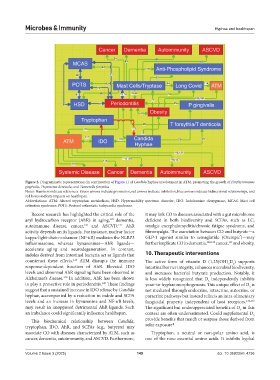
Figure 2. Diagrammatic representation (in continuation of Figure 1) of Candida hyphae involvement in ATM, promoting the growth of Porphyromonas
gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia
Notes: Numbers indicate references. Green arrows indicate promotion, red arrows indicate inhibition, blue arrows indicate bidirectional relationships, and
red boxes indicate impacts on healthspan.
Abbreviations: ATM: Altered tryptophan metabolism; HSD: Hypermobility spectrum disorder; IDO: Indoleamine dioxygenase; MCAS: Mast cell
activation syndrome; POTS: Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.
Recent research has highlighted the critical role of the it may link CO to diseases associated with a gut microbiome
aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in aging, dementia, deficient in both biodiversity and SCFAs, such as LC,
125
autoimmune disease, cancer, and ASCVD. AhR myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome, and
127
126
activity depends on its ligands. For instance, nuclear factor fibromyalgia. The association between CO and butyrate—a
kappa-light-chain-enhancer (NF-κB) mediates the NLRP3 GLP-1 agonist similar to semaglutide (Ozempic )—may
®
inflammasome, whereas kynurenines—AhR ligands— further implicate CO in dementia, 129,130 cancer, and obesity.
131
accelerate aging and neurodegeneration. In contrast,
indoles derived from intestinal bacteria act as ligands that 10. Therapeutic interventions
counteract these effects. ATM disrupts the immune The active form of vitamin D (1,25(OH) D ) supports
125
3
2
response-dependent function of AhR. Elevated IDO intestinal barrier integrity, enhances microbial biodiversity,
levels and abnormal AhR signaling have been observed in and increases bacterial butyrate production. Notably, it
Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, AhR has been shown is less widely recognized that D independently inhibits
120
3
to play a protective role in periodontitis. These findings yeast-to-hyphae morphogenesis. This unique effect of D is
128
3
suggest that a sustained increase in IDO release by Candida not mediated through endocrine, intracrine, autocrine, or
hyphae, accompanied by a reduction in indole and SCFA paracrine pathways but instead reflects an intra-alimentary
levels and an increase in kynurenine and NF-κB levels, fungicidal property independent of host receptors. 132,133
may result in unopposed detrimental AhR ligands. Such The significant but underappreciated benefits of D in this
3
an imbalance could significantly influence healthspan. context are often underestimated. Could supplemental D
3
This biochemical relationship between Candida, provide benefits that match or surpass those derived from
tryptophan, IDO, AhR, and SCFAs (e.g., butyrate) may solar exposure?
associate CO with diseases characterized by ATM, such as Tryptophan, a neutral or non-polar amino acid, is
cancer, dementia, autoimmunity, and ASCVD. Furthermore, one of the nine essential amino acids. It inhibits hyphal
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 149 doi: 10.36922/mi.4736