Page 40 - MI-2-3
P. 40
Microbes & Immunity Probiotics from ancient wisdom to modern days
pollutants in water, air, and soil, helping in the
degradation of pollutants, such as hydrocarbons,
heavy metals, and synthetic dyes.
• Food industry: Microorganisms are used in the
production of fermented foods and beverages, which
offer various health benefits. They are involved in
the fermentation of dairy and non‐dairy products,
enhancing flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
• Probiotics and health: Probiotics, which are beneficial
microorganisms, play a significant role in maintaining
gut health and overall well‐being. They can help
in restoring healthy microbiome communities and
preventing infections.
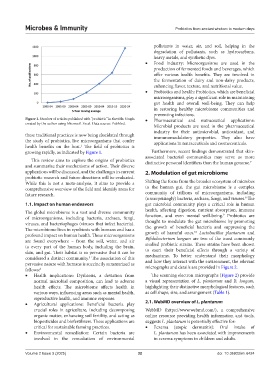
Figure 1. Number of articles published with “probiotic” in the title. Graph • Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications:
created by the author using Microsoft Excel. Data source: PubMed.
Microbial products are used in the pharmaceutical
industry for their antimicrobial, antioxidant, and
these traditional practices is now being elucidated through immunomodulatory properties. They also have
the study of probiotics, live microorganisms that confer applications in nutraceuticals and cosmeceuticals.
1
health benefits on the host. The field of probiotics is
growing rapidly, as indicated by Figure 1. Furthermore, recent findings demonstrated that skin-
associated bacterial communities may serve as more
This review aims to explore the origins of probiotics distinctive personal identifiers than the human genome. 7
and summarize their mechanisms of action. Their diverse
applications will be discussed, and the challenges in current 2. Modulation of gut microbiome
probiotic research and future directions will be evaluated.
While this is not a meta-analysis, it aims to provide a Shifting the focus from the broader ecosystem of microbes
comprehensive overview of the field and identify areas for to the human gut, the gut microbiome is a complex
future research. community of trillions of microorganisms, including
(unsurprisingly) bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses. The
8
1.1. Impact on human endeavors gut microbial community plays a critical role in human
health, affecting digestion, nutrient absorption, immune
The global microbiome is a vast and diverse community 9
of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, function, and even mental well-being. Probiotics are
viruses, and bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria). thought to modulate the gut microbiome by promoting
The microbiome lives in symbiosis with humans and has a the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppressing the
10
profound impact on human health. These microorganisms growth of harmful ones. Lactobacillus plantarum and
are found everywhere – from the soil, water, and air Bifidobacterium longum are two of the most commonly
to every part of the human body, including the brain, studied probiotic strains. These strains have been shown
to exert their beneficial effects through a variety of
skin, and gut. Their habitat is so pervasive that it can be
considered a distinct community. The association of this mechanisms. To better understand their morphology
5
pervasive nature with humans is succinctly summarized as and how they interact with the environment, the relevant
follows: 6 micrographs and details are provided in Figure 2.
• Health implications: Dysbiosis, a deviation from The scanning electron micrographs (Figure 2) provide
normal microbial composition, can lead to adverse a visual representation of L. plantarum and B. longum,
health effects. The microbiome affects health in highlighting their distinctive morphological features, such
various ways, influencing areas such as mental health, as cell shape, size, and arrangement (Table 1).
reproductive health, and immune response.
• Agricultural applications: Beneficial bacteria play 2.1. WebMD overview of L. plantarum
crucial roles in agriculture, including decomposing WebMD (https://www.webmd.com/), a comprehensive
organic matter, enhancing soil fertility, and acting as online resource providing health information and tools,
biopesticides and biofertilizers. These applications are suggests L. plantarum is potentially effective for:
critical for sustainable farming practices. • Eczema (atopic dermatitis): Oral intake of
• Environmental remediation: Certain bacteria are L. plantarum has been associated with improvements
involved in the remediation of environmental in eczema symptoms in children and adults.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 32 doi: 10.36922/mi.6424