Page 11 - MI-2-4
P. 11
Microbes & Immunity Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus CP biosynthesis
A
B
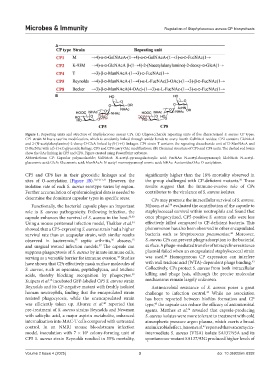
Figure 1. Repeating units and structure of Staphylococcus aureus CPs. (A) Oligosaccharide repeating units of five characterized S. aureus CP types.
CP1 strain M has a taurine modification, which is covalently linked through amide bonds to every fourth GalNAcA residue. CP2 contains GlcNAcA
and 2-(N-acetylalanylamino)-2-deoxy-D-GlcA linked by β-(1→4) linkages. CP4 strain T contains the repeating disaccharide unit of D-ManNAcA and
D-FucNAc with a β-(1→3) glycosidic linkage. CP5 and CP8 carry OAc modifications. (B) Chemical structure of CP5 and CP8 units. The dashed red boxes
show the OAc linking in CP5 and CP8. Figure created using PowerPoint software.
Abbreviations: CP: Capsular polysaccharide; GalNAcA: N-acetyl-pyranogalactosylic acid; FucNAc: N-acetyl-fucopyranosyl; GlcNAcA: N-acetyl-
glucuronic acid; GlcA: Glucuronic acid; ManNAcA: N-acetyl-mannopyranosyl uronic acid; NHAc: Acetamido; OAc: O-acetylation.
CP5 and CP8 lies in their glycosidic linkages and the significantly higher than the 18% mortality observed in
sites of O-acetylation (Figure 1B). 10,14,17,31 However, the the group challenged with CP-deficient mutants. These
36
isolation rate of each S. aureus serotype varies by region. results suggest that the immune-evasive role of CPs
Further accumulation of epidemiological data is needed to contributes to the virulence of S. aureus isolates.
determine the dominant capsular types in specific areas. CPs may promote the intracellular survival of S. aureus.
Functionally, the bacterial capsule plays an important Nilsson et al. evaluated the contribution of the capsule to
36
role in S. aureus pathogenicity. Following infection, the staphylococcal survival within neutrophils and found that
capsule enhances the survival of S. aureus in the host. 32,33 once phagocytized, CP5-positive S. aureus cells were less
Using a mouse peritoneal infection model, Thakker et al. effectively killed compared to CP-deficient bacteria. This
34
showed that a CP5-expressing S. aureus strain had a higher phenomenon has also been observed in other encapsulated
41
survival rate than an acapsular strain, with similar results bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae. Moreover,
observed in bacteremia, septic arthritis, abscess, S. aureus CPs can prevent phage adsorption to the bacterial
15
36
35
and surgical wound infection models. The capsule can surface. A phage-mediated transfer of tetracycline resistance
37
suppress phagocytosis of S. aureus by innate immune cells, plasmid failed when an encapsulated staphylococcal strain
42
serving as a versatile barrier for immune evasion. Studies was used. Homogeneous CP expression can interfere
38
43
have shown that CPs effectively mask surface molecules of with wall teichoic acid (WTA)-dependent phage binding.
S. aureus, such as opsonins, peptidoglycan, and teichoic Collectively, CPs protect S. aureus from both intracellular
acids, thereby blocking recognition by phagocytes. killing and phage lysis, although the precise molecular
39
Kuipers et al. incubated GFP-labeled CP5 S. aureus strain mechanisms remain largely unknown.
38
Reynolds and its CP-negative mutant with freshly isolated Antimicrobial resistance of S. aureus poses a great
human neutrophils, finding that the encapsulated strain challenge to infection control. While no association
44
resisted phagocytosis, while the unencapsulated strain has been reported between biofilm formation and CP
was efficiently taken up. Alvarez et al. reported that type, the capsule can reduce the efficacy of antimicrobial
40
45
pre-treatment of S. aureus strains Reynolds and Newman agents. Matthes et al. revealed that capsule-producing
46
with salicylic acid, a major aspirin metabolite, enhanced S. aureus isolates were more tolerant to treatment with cold
internalization into MAC-T cells compared with untreated atmospheric pressure argon plasma, which exerts a broad
control. In an NMRI mouse bloodstream infection antimicrobial effect. Jansen et al. reported that vancomycin-
47
6
model, inoculation with 7 × 10 colony-forming unit of intermediate S. aureus (VISA) isolate SA137/93A and its
CP5 S. aureus strain Reynolds resulted in 55% mortality, spontaneous-mutant SA137/93G produced higher levels of
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/mi.8392