Page 14 - MI-2-4
P. 14
Microbes & Immunity Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus CP biosynthesis
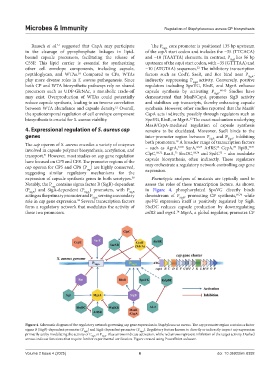
Rausch et al. suggested that CapA may participate The P SigA core promoter is positioned 135 bp upstream
31
in the cleavage of pyrophosphate linkages in lipid- of the capA start codon and includes the −35 (TTCACA)
bound capsule precursors, facilitating the release of and −10 (TAATTA) elements. In contrast, P SigB lies 56 bp
C55P. This lipid carrier is essential for synthesizing upstream of the capA start codon, with −35 (GTTTAA) and
other cell envelope components, including capsule, −10 (ATGTAA) sequences. The inhibitory transcription
22
peptidoglycan, and WTAs. Compared to CPs, WTAs factors such as CodY, SaeR, and Rot bind near P SigA ,
14
play more diverse roles in S. aureus pathogenesis. Since indirectly suppressing P SigB activity. Conversely, positive
both CP and WTA biosynthetic pathways rely on shared regulators including SpoVG, RbsR, and MgrA enhance
precursors such as UDP-GlcNAc, a metabolic trade-off capsule synthesis by activating P SigB . 60-62 Studies have
may exist. Overproduction of WTAs could potentially demonstrated that MsaB/CspA promotes SigB activity
reduce capsule synthesis, leading to an inverse correlation and stabilizes cap transcripts, thereby enhancing capsule
between WTA abundance and capsule density. Overall, synthesis. However, other studies reported that the MsaB/
12
the spatiotemporal regulation of cell envelope component CspA acts indirectly, possibly through regulators such as
biosynthesis is crucial for S. aureus viability. SpoVG, RbsR, or MgrA. The exact mechanism underlying
63
MsaB/CspA-mediated regulation of capsule synthesis
4. Expressional regulation of S. aureus cap remains to be elucidated. Moreover, SaeR binds to the
genes inter-promoter region between P SigB and P SigA , inhibiting
18
The cap operon of S. aureus encodes a variety of enzymes both promoters. A broader range of transcription factors
70,71
69
66,67
64,65
68
involved in capsule polymer biosynthesis, acetylation, and – such as AgrA, SarA, ArlRS, CcpA, RpiR,
73
68,72
75
68,74
31
transport. However, most studies on cap gene regulation ClpC, RsaA, SbcDC, and SpdC – also modulate
have focused on CP5 and CP8. The promoter regions of the capsule biosynthesis, often indirectly. These regulators
cap operon for CP5 and CP8 (P ) are highly conserved, may orchestrate a regulatory network controlling cap gene
cap
suggesting similar regulatory mechanisms for the expression.
58
expression of capsule synthesis genes in both serotypes. Phenotypic analyses of mutants are typically used to
Notably, the P contains sigma factor B (SigB)-dependent assess the roles of these transcription factors. As shown
cap
(P SigB ) and SigA-dependent (P SigA ) promoters, with P SigB in Figure 4, phosphorylated SpoVG directly binds
acting as the primary promoter and P SigA serving a secondary downstream of P SigB , promoting CP synthesis, 60,76 while
role in cap gene expression. Several transcription factors spoVG expression itself is positively regulated by SigB.
59
form a regulatory network that modulates the activity of SbcDC reduces capsule production by downregulating
these two promoters. arlRS and mgrA. MgrA, a global regulator, promotes CP
74
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the regulatory network governing cap gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus. The cap promoter region contains a factor
sigma B (SigB)-dependent promoter (P SigB ) and SigA-dependent promoter (P SigA ). Regulatory factors known to directly or indirectly impact cap expression
primarily act by modulating the activity of P SigB or P SigA . Blue arrows indicate activation, while red arrows represent inhibition of the target activity. Dashed
arrows indicate functions that require further experimental verification. Figure created using PowerPoint software.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/mi.8392