Page 26 - MI-2-4
P. 26
Microbes & Immunity Infectious agents and autoimmune diseases
misdirection by infectious agents (bacteria, viruses,
etc.), often in conjunction with environmental factors.
Current mainstream treatments aimed at relieving
symptoms are mainly based on immunosuppressive or
8
immunomodulatory drugs. Despite these advances, the
precise mechanism and etiology of autoimmune diseases
remain unclear. 9
This paper is focused on the mechanism that underlies
the autoimmune response. A general conceptual model
and evidence supporting its plausibility are outlined
and discussed. Moreover, several new explanations of
autoimmune response features that can be derived from
the model are presented and briefly discussed. Finally,
research directions aimed at the development of new
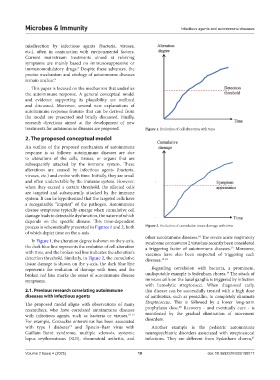
treatments for autoimmune diseases are proposed. Figure 1. Evolution of cell alteration with time
2. The proposed conceptual model
An outline of the proposed mechanism of autoimmune
response is as follows: autoimmune diseases are due
to alterations of the cells, tissues, or organs that are
subsequently attacked by the immune system. These
alterations are caused by infectious agents (bacteria,
viruses, etc.) and evolve with time. Initially, they are small
and often undetectable by the immune system. However,
when they exceed a certain threshold, the affected cells
are targeted and subsequently attacked by the immune
system. It can be hypothesized that the targeted cells have
a recognizable “imprint” of the pathogen. Autoimmune
disease symptoms typically emerge when cumulative cell
damage leads to detectable dysfunction, the nature of which
depends on the specific disease. This time-dependent
process is schematically presented in Figures 1 and 2, both Figure 2. Evolution of cumulative tissue damage with time
of which depict time on the x-axis.
14
other autoimmune diseases. The severe acute respiratory
In Figure 1, the alteration degree is shown on the y-axis, syndrome coronavirus 2 virus has recently been considered
the dark blue line represents the evolution of cell alteration a triggering factor of autoimmune diseases. Moreover,
15
with time, and the broken red line indicates the alteration’s vaccines have also been suspected of triggering such
detection threshold. Similarly, in Figure 2, the cumulative diseases. 16-18
tissue damage is shown on the y-axis, the dark blue line
represents the evolution of damage with time, and the Regarding correlation with bacteria, a prominent,
19
broken red line marks the onset of autoimmune disease undisputable example is Sydenham chorea. The attack of
symptoms. immune cells on the basal ganglia is triggered by infection
with hemolytic streptococci. When diagnosed early,
2.1. Previous research correlating autoimmune this disease can be successfully treated with a high dose
diseases with infectious agents of antibiotics, such as penicillin, to completely eliminate
The proposed model aligns with observations of many Streptococcus. This is followed by a lower long-term
20
researchers, who have correlated autoimmune diseases prophylaxis dose. Recovery - and eventually cure - is
with infectious agents, such as bacteria or viruses. 10-12 manifested by the gradual elimination of movement
For example, Coxsackie enterovirus has been associated disorders.
with type 1 diabetes and Epstein–Barr virus with Another example is the pediatric autoimmune
13
Guillain–Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis, systemic neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal
lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and infections. They are different from Sydenham chorea,
21
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 18 doi: 10.36922/MI025100017