Page 100 - MSAM-2-4
P. 100
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing 3D-printed composite auxetic structures
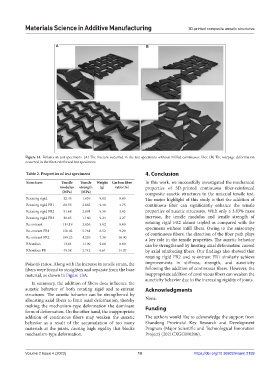
A B
Figure 14. Failures in test specimens. (A) The fracture occurred in the test specimens without infilled continuous fiber. (B) The warpage deformation
occurred in the fiber-reinforced test specimens.
Table 2. Properties of test specimens 4. Conclusion
Structures Tensile Tensile Weight Carbon fiber In this work, we successfully investigated the mechanical
modulus strength (g) ratio (%) properties of 3D-printed continuous fiber-reinforced
(MPa) (MPa) composite auxetic structures in the uniaxial tensile test.
Rotating rigid 22.45 1.039 9.03 0.00 The major highlight of this study is that the addition of
Rotating rigid FR1 60.55 2.883 9.48 4.75 continuous fiber can significantly enhance the tensile
Rotating rigid FR2 51.68 2.891 9.39 3.83 properties of auxetic structures. With only a 3.83% mass
Rotating rigid FR3 30.65 1.180 9.24 2.27 increase, the tensile modulus and tensile strength of
Re-entrant 114.19 2.836 5.92 0.00 rotating rigid FR2 almost tripled as compared with the
Re-entrant FR1 150.02 5.781 6.52 9.20 specimens without infill fibers. Owing to the anisotropy
of continuous fibers, the direction of the fiber path plays
Re-entrant FR2 189.25 4.229 7.30 18.90 a key role in the tensile properties. The auxetic behavior
Rhombus 13.64 1.109 5.68 0.00 can be strengthened by limiting axial deformation caused
Rhombus FR 49.58 2.742 6.61 14.07 by axial reinforcing fibers. Our findings also showed that
rotating rigid FR2 and re-entrant FR1 similarly achieve
Poison’s ratios. Along with the increase in tensile strain, the improvements in stiffness, strength, and auxeticity
fibers were found to straighten and separate from the base following the addition of continuous fibers. However, the
material, as shown in Figure 13A. inappropriate addition of continuous fibers can weaken the
auxeticity behavior due to the increasing rigidity of joints.
In summary, the addition of fibers does influence the
auxetic behavior of both rotating rigid and re-entrant Acknowledgments
structures. The auxetic behavior can be strengthened by
allocating axial fibers to limit axial deformation, thereby None.
making the mechanism-type deformation the dominant Funding
form of deformation. On the other hand, the inappropriate
addition of continuous fibers may weaken the auxetic The authors would like to acknowledge the support from
behavior as a result of the accumulation of too many Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development
materials at the joints, causing high rigidity that blocks Program (Major Scientific and Technological Innovation
mechanism-type deformation. Project) (2021CXGC010206).
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2159