Page 10 - MSAM-3-1
P. 10
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Preparation and modification of porous Ti
design factors of porous implant unit structure, pore size, the powder surface through compaction, sintering, and
porosity, and pore distribution. 29 other processes to obtain porous metal (Figure 3A). The
35
The material’s surface is in direct contact with cells and structure and mechanical properties of porous titanium
tissues, and the surface properties are related to the interface alloys obtained by this process are affected by sintering
bonding between materials and tissues. In addition, surface temperature, time, pressure, powder composition/particle
36
roughness or morphology and element release directly size, and other factors.
affect gene expression and protein synthesis inside cells. Oh et al. studied the effect of powder diameter on
37
Therefore, surface properties are important factors affecting porous titanium’s morphology and mechanical properties.
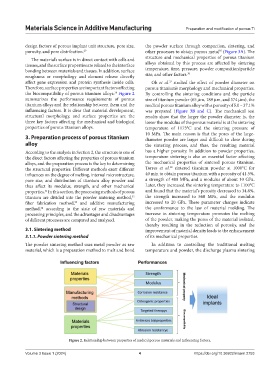
the biocompatibility of porous titanium alloys. Figure 2 By controlling the sintering conditions and the particle
30
summarizes the performance requirements of porous size of titanium powder (65 μm, 189 μm, and 374 μm), the
titanium alloys and the relationship between them and the medical porous titanium alloy with a porosity of 5.0 – 37.1%
influencing factors. It is clear that material development, was prepared (Figure 3B and C). The mechanical test
structural morphology, and surface properties are the results show that the larger the powder diameter is, the
three key factors affecting the mechanical and biological lower the modulus of the porous material is at the sintering
properties of porous titanium alloys. temperature of 1173°C and the sintering pressure of
10 MPa. The main reason is that the pores of the large-
3. Preparation process of porous titanium diameter powder are larger and difficult to close during
alloy the sintering process, and thus, the resulting material
According to the analysis in Section 2, the structure is one of has a higher porosity. In addition to powder properties,
the direct factors affecting the properties of porous titanium temperature sintering is also an essential factor affecting
alloys, and the preparation process is the key to determining the mechanical properties of sintered porous titanium.
38
the structural properties. Different methods exert different Torres et al. sintered titanium powder at 1000°C for
influences on the degree of melting, internal microstructure, 40 min to obtain porous titanium with a porosity of 41.5%,
pore size, and distribution of titanium alloy powder and a strength of 480 MPa, and a modulus of about 10 GPa.
thus affect its modulus, strength, and other mechanical Later, they increased the sintering temperature to 1100°C
properties. In this section, the processing methods of porous and found that the material’s porosity decreased to 34.6%,
31
titanium are divided into the powder sintering method, the strength increased to 560 MPa, and the modulus
32
fiber fabrication method, and additive manufacturing increased to 20 GPa. These parameter changes indicate
33
method, according to the state of raw materials and the conformance to the law of material molding. The
34
processing principles, and the advantages and disadvantages increase in sintering temperature promotes the melting
of different processes are compared and analyzed. of the powder, making the pores of the material isolated,
thereby resulting in the reduction of porosity, and the
3.1. Sintering method improvement of material density leads to the enhancement
3.1.1. Powder sintering method of its mechanical properties.
The powder sintering method uses metal powder as raw In addition to controlling the traditional melting
material, which is a preparation method to melt and bond temperature and powder, the discharge plasma sintering
Figure 2. Relationship between properties of medical porous materials and influencing factors.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2753