Page 11 - MSAM-3-1
P. 11
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Preparation and modification of porous Ti
A
B C
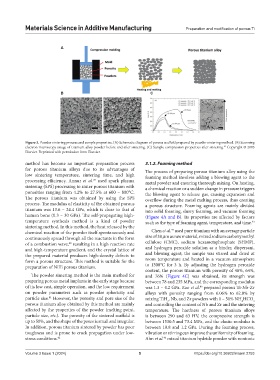
Figure 3. Powder sintering process and sample properties. (A) Schematic diagram of porous scaffold prepared by powder sintering method. (B) Scanning
electron microscopy image of titanium alloy powder before and after sintering. (C) Sample compression properties after sintering. Copyright © 2003
37
Elsevier. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier.
method has become an important preparation process 3.1.2. Foaming method
for porous titanium alloys due to its advantages of The process of preparing porous titanium alloy using the
low sintering temperature, sintering time, and high foaming method involves adding a blowing agent to the
processing efficiency. Annur et al. used spark plasma metal powder and ensuring thorough mixing. On heating,
39
sintering (SPS) processing to sinter porous titanium with a chemical reaction or a sudden change in pressure triggers
porosities ranging from 4.2% to 27.5% at 600 – 800°C. the blowing agent to release gas, causing expansion and
The porous titanium was obtained by using the SPS overflow during the metal melting process, thus creating
process. The modulus of elasticity of the obtained porous a porous structure. Foaming agents are mainly divided
titanium was 13.6 – 24.4 GPa, which is close to that of into solid foaming, slurry foaming, and vacuum foaming
human bone (0.3 – 30 GPa). The self-propagating high- (Figure 4A and B). Its properties are affected by factors
temperature synthesis method is a kind of powder such as the type of foaming agent, temperature, and time. 43
sintering method. In this method, the heat released by the
44
chemical reaction of the powder itself spontaneously and Chen et al. used pure titanium with an average particle
continuously spread through all the reactants in the form size of 38 μm as raw material, mixed sodium carboxymethyl
of a combustion wave, resulting in a high reaction rate cellulose (CMC), sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP),
40
and high-temperature gradient, and the crystal lattice of and hydrogen peroxide solution as a binder, dispersant,
the prepared material produces high-density defects to and blowing agent; the sample was stirred and dried at
form a porous structure. This method is suitable for the room temperature and heated in a vacuum atmosphere
preparation of NiTi porous titanium. to 1300°C for 3 h. By adjusting the hydrogen peroxide
content, the porous titanium with porosity of 48%, 64%,
The powder sintering method is the main method for and 76% (Figure 4C) was obtained, its strength was
preparing porous metal implants in the early stage because between 78 and 235 MPa, and the corresponding modulus
of its low cost, simple operation, and the low requirement was 1.3 – 4.2 GPa. Rao et al. prepared porous Ti-Nb-Zr
45
on powder parameters such as powder sphericity and alloys with porosity ranging from 6.06% to 62.8% by
particle size. However, the porosity and pore size of the mixing TiH , Nb, and Zr powders with 0 – 50% NH HCO
41
4
2
3
porous titanium alloy obtained by this method are mainly and controlling the content of Nb and Zr and the sintering
affected by the properties of the powder (melting point, temperature. The hardness of porous titanium alloys
particle size, etc.). The porosity of the sintered scaffold is is between 290 and 63 HV, the compressive strength is
up to 50%, and the shape of the pores is small and irregular. between 1530.5 and 73.4 MPa, and the elastic modulus is
In addition, porous titanium sintered by powder has poor between 10.8 and 1.2 GPa. During the foaming process,
toughness and is prone to crack propagation under low- vibration or stirring can improve the uniformity of foaming.
stress conditions. 42 Ahn et al. mixed titanium hydride powder with nonionic
46
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2753