Page 16 - MSAM-3-1
P. 16
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Preparation and modification of porous Ti
A B
C
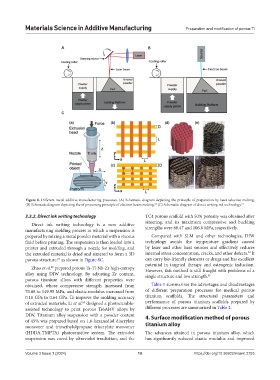
Figure 8. Different metal additive manufacturing processes. (A) Schematic diagram depicting the principle of preparation by laser selective melting.
(B) Schematic diagram depicting the of processing principle of electron beam melting. (C) Schematic diagram of direct writing ink technology. 67
66
3.3.2. Direct ink writing technology TC4 porous scaffold with 50% porosity was obtained after
sintering, and its maximum compressive and buckling
Direct ink writing technology is a new additive
manufacturing molding process in which a suspension is strengths were 60.47 and 106.8 MPa, respectively.
prepared by mixing a metal powder material with a viscous Compared with SLM and other technologies, DIW
fluid before printing. The suspension is then loaded into a technology avoids the temperature gradient caused
printer and extruded through a nozzle for molding, and by laser and other heat sources and effectively reduces
84
the extruded material is dried and sintered to form a 3D internal stress concentration, cracks, and other defects. It
81
porous structure, as shown in Figure 8C. can carry bio-friendly elements or drugs and has excellent
potential in targeted therapy and osteogenic induction.
Zhao et al. prepared porous Ta-Ti-Nb-Zr high-entropy However, this method is still fraught with problems of a
82
alloy using DIW technology. By adjusting Zr content, single structure and low strength. 85
porous titanium alloys with different properties were
obtained, whose compressive strength increased from Table 1 summarizes the advantages and disadvantages
70.08 to 149.95 MPa, and elastic modulus increased from of different preparation processes for medical porous
0.18 GPa to 0.64 GPa. To improve the molding accuracy titanium scaffolds. The structural parameters and
of extruded materials, Li et al. designed a photocurable- performance of porous titanium scaffolds prepared by
83
assisted technology to print porous Ti6Al4V alloys by different processes are summarized in Table 2.
DIW. Titanium alloy suspension with a powder content 4. Surface modification method of porous
of 45% was prepared based on 1,6-hexanediol diacrylate
monomer and trimethylolpropane triacrylate monomer titanium alloy
(HDDA-TMPTA) photosensitive system. The extruded The advances attained in porous titanium alloy, which
suspension was cured by ultraviolet irradiation, and the has significantly reduced elastic modulus and improved
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2753