Page 17 - MSAM-3-1
P. 17
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Preparation and modification of porous Ti
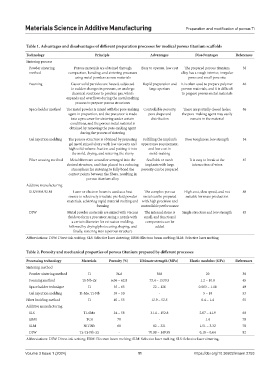
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of different preparation processes for medical porous titanium scaffolds
Technology Principle Advantages Disadvantages References
Sintering process
Powder sintering Porous materials are obtained through Easy to operate, low cost The prepared porous titanium 38
method compaction, bonding, and sintering processes alloy has a rough interior, irregular
using metal powders as raw materials pores and small pore size
Foaming Gas or solid particles are heated, subjected Rapid preparation and It is often used to prepare polymer 46
to sudden changes in pressure, or undergo large aperture porous materials, and it is difficult
chemical reactions to produce gas, which to prepare porous metal materials
expands and overflows during the metal melting
process to prepare porous structures
Space holder method The metal powder is mixed with the pore-making Controllable porosity, There are partially closed holes; 86
agent in proportion, and the precursor is made pore shape and the pore-making agent may easily
into a precursor for sintering under certain distribution remain in the material
conditions, and the porous metal material is
obtained by removing the pore-making agent
during the process of sintering
Gel injection molding The porous structure is obtained by preparing Fulfilling the implant’s Poor toughness, low strength 54
gel metal mixed slurry with low viscosity and appearance requirement,
high solid volume fraction and putting it into and low cost in
the mold, drying, and sintering the slurry mold-making
Fiber weaving method Metal fibers are wound or arranged into the Scaffolds or mesh It is easy to break at the 87
desired structure, and then placed in a reducing implants with large intersection of wires
atmosphere for sintering to fully bond the porosity can be prepared
contact points between the fibers, resulting in
porous titanium alloy
Additive manufacturing
SLS/EBM/SLM Laser or electron beam is used as a heat The complex porous High cost, slow speed, and not 88
source to selectively irradiate pre-laid powder metal can be prepared suitable for mass production
materials, achieving rapid material melting and with high precision and
forming controllable performance
DIW Metal powder materials are mixed with viscous The internal stress is Single structure and low strength 83
fluids to form a precursor, using a nozzle with small, and functional
a certain diameter for extrusion molding, components can be
followed by drying/photocuring shaping, and added
finally, sintering into a porous structure
Abbreviations: DIW: Direct ink writing; SLS: Selective laser sintering; EBM: Electron beam melting; SLM: Selective laser melting.
Table 2. Porosity and mechanical properties of porous titanium prepared by different processes
Processing technology Materials Porosity (%) Ultimate strength (MPa) Elastic modulus (GPa) References
Sintering method
Powder sintering method Ti 34.6 560 20 38
Foaming method Ti-Nb-Zr 6.06 – 62.8 73.4 – 1530.5 1.2 – 10.8 45
Space holder technique Ti 35 – 65 22 – 126 0.063 – 1.18 49
Gel injection molding Ti-Mo, Ti-Nb 39 – 50 - 5 – 18 53
Fiber braiding method Ti 40 – 55 12.9 – 52.5 0.4 – 1.4 55
Additive manufacturing
SLS Ti-6Mo 24 – 58 31.4 – 152.8 2.07 – 41.9 60
EBM TC4 70 - 1.4 70
SLM NiTiNb 60 82 – 321 1.51 – 3.32 78
DIW Ta-Ti-Nb-Zr - 70.08 – 149.95 0.18 – 0.64 82
Abbreviations: DIW: Direct ink writing; EBM: Electron beam melting; SLM: Selective laser melting; SLS: Selective laser sintering.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 11 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2753