Page 50 - MSAM-3-4
P. 50
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Directed energy deposition
A B
Figure 4. Coating Characterization. (A) X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra of the coatings. (B) Carbon content of the coatings
Abbreviations: B-DED: Broad-beam laser-directed energy deposition; H-DED: High-speed directed energy deposition
maximum have enhanced. In the B-DED coating, the most A B
robust diffraction peak shifts from the (111) crystal face to
the (200) crystal face, indicating a change in the preferred
orientation of the surface grains. Figure 4B shows the
26
carbon content calculated based on XRD results. The
carbon content of the powder is zero. The carbon content
of the coatings varies with different processing methods, C D
indicating that the substrate dilutes the coating to different
extents. The higher carbon content in the B-DED coating
suggests a stronger dilution effect from the matrix, which
can lead to a degradation in its performance.
3.3. Microstructure of the coatings
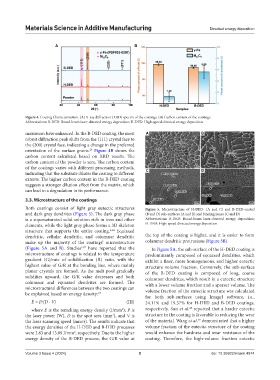
Both coatings consist of light gray eutectic structures Figure 5. Microstructure of H-DED- (A and C) and B-DED-coated
and dark gray dendrites (Figure 5). The dark gray phase (B and D) sub-surfaces (A and B) and binding zones (C and D)
is a supersaturated solid solution rich in iron and other Abbreviations: B-DED: Broad-beam laser-directed energy deposition;
elements, while the light gray phase forms a 3D skeleton H-DED: High-speed directed energy deposition
structure that supports the entire coating. 2,24 Equiaxed
dendritic, cellular dendritic, and columnar dendritic the top of the coating is higher, and it is easier to form
make up the majority of the coatings’ microstructure columnar dendritic protrusions (Figure 5B).
(Figure 5A and B). Studies 1,27 have reported that the In Figure 5A, the sub-surface of the H-DED coating is
microstructure of coatings is related to the temperature predominantly composed of equiaxed dendrites, which
gradient (G)/rate of solidification (R) ratio, with the exhibit a finer, more homogeneous, and higher eutectic
highest value of G/R at the bonding line, where mainly structure volume fraction. Conversely, the sub-surface
planar crystals are formed. As the melt pool gradually of the B-DED coating is composed of long, coarse
solidifies upward, the G/R value decreases and both columnar dendrites, which result in a eutectic structure
columnar and equiaxed dendrites are formed. The with a lower volume fraction and a sparser volume. The
microstructural differences between the two coatings can volume fraction of the eutectic structure was calculated
be explained based on energy density: 24
for both sub-surfaces using ImageJ software, i.e.,
E = P/(D · V) (III) 24.11% and 19.37% for H-DED and B-DED coatings,
28
where E is the remelting energy density (J/mm ), P is respectively. Sun et al. reported that a harder eutectic
2
the laser power (W), D is the spot area (mm ), and V is structure in the coating is favorable to reducing the wear
2
the laser scanning speed (mm/s). The results indicate that of the material. Wang et al. demonstrated that a higher
29
the energy densities of the H-DED and B-DED processes volume fraction of the eutectic structure of the coating
were 2.83 and 13.89 J/mm , respectively. Due to the higher would enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the
2
energy density of the B-DED process, the G/R value at coating. Therefore, the high-volume fraction eutectic
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/msam.4974