Page 12 - MSAM-4-2
P. 12
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Hydrogels in mandibular reconstruction
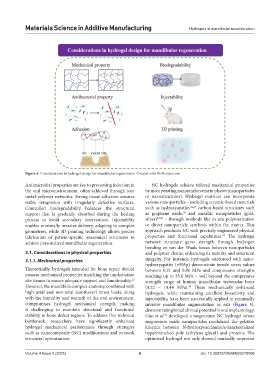
Figure 4. Considerations in hydrogel design for mandibular regeneration. Created with BioRender.com
Antimicrobial properties are key to preventing infection in NC hydrogels achieve tailored mechanical properties
the oral microenvironment, often achieved through ion/ by incorporating nanoreinforcement phases (nanoparticles
metal-polymer networks. Strong tissue adhesion ensures or nanostructures). Hydrogel matrices can incorporate
stable integration with irregularly defective surfaces. various nanoparticles – including ceramic-based materials
Controlled biodegradability balances the structural such as hydroxyapatite, 24,25 carbon-based structures such
26
support that is gradually absorbed during the healing as graphene oxide, and metallic nanoparticles (gold,
process to avoid secondary intervention. Injectability silver) 27,28 – through methods like in situ polymerization
enables minimally invasive delivery, adapting to complex or direct nanoparticle synthesis within the matrix. This
geometries, while 3D printing technology allows precise approach produces NC with precisely engineered physical
29
fabrication of patient-specific anatomical structures to properties and functional capabilities. The hydrogel
achieve personalized mandibular regeneration. network structure gains strength through hydrogen
bonding or van der Waals forces between nanoparticles
3.1. Considerations in physical properties and polymer chains, enhancing its stability and structural
3.1.1. Mechanical properties integrity. For instance, hydrogels reinforced with nano-
hydroxyapatite (nHAp) demonstrate tensile stress values
Theoretically, hydrogels intended for bone repair should between 0.21 and 0.86 MPa and compressive strengths
possess mechanical properties matching the implantation reaching up to 35.8 MPa – well beyond the compressive
23
site tissues to ensure adequate support and functionality. strength range of human mandibular trabecular bone
However, the mandible’s complex anatomy, combined with (0.22 – 10.44 MPa). These mechanically enhanced
30
high axial and non-axial (cantilever) stress loads, along hydrogels, while maintaining excellent bioactivity and
with the humidity and warmth of the oral environment, injectability, have been successfully applied in minimally
compromises hydrogel mechanical strength, making invasive mandibular augmentation in rats (Figure 5),
it challenging to maintain structural and functional demonstrating broad clinical potential in oral implantology.
stability in bone defect regions. To address this technical Guo et al. developed a magnesium NC hydrogel where
31
bottleneck, researchers have significantly enhanced magnesium oxide nanoparticles modulated the gelation
hydrogel mechanical performance through strategies kinetics between N-hydroxysuccinimide-functionalized
such as nanocomposite (NC) modifications and network hyperbranched poly (ethylene glycol) and proteins. The
structural optimization. optimized hydrogel not only showed markedly improved
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/MSAM025070006