Page 8 - MSAM-4-2
P. 8
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Hydrogels in mandibular reconstruction
1. Introduction Recent years have witnessed remarkable progress in
bioactive materials. Hydrogels have garnered particular
The mandible, as a crucial load-bearing structure in attention due to their exceptional biocompatibility,
the craniofacial complex, not only maintains facial tunable properties, and potential to mimic the natural
contours but also supports vital physiological functions extracellular matrix (ECM) of mandibular bone. Through
such as mastication, swallowing, and speech. Clinically,
mandibular defects primarily arise from pathological incorporation of bioactive factors (bone morphogenetic
2
processes including head and neck tumor resection, protein 2 [BMP- , vascular endothelial growth factor
traumatic fractures, osteoradionecrosis, and medication- [VEGF]) and mesenchymal stem cells, hydrogels can
1,2
related osteonecrosis of the jaw, often resulting in create biomimetic microenvironments conducive to
maxillofacial deformities and functional impairments osteoblast migration and ordered differentiation of bone
5,6
of mastication and swallowing. However, mandibular progenitor cells. Compared to traditional implants,
regeneration remains challenging due to irregular defect their minimally invasive injectability effectively avoids
geometry, high functional restoration requirements, and secondary surgery risks, while adjustable crosslinking
complex healing environments. While small-sized bone density enables spatiotemporal control of degradation
defects demonstrate self-healing capacity, critical-sized kinetics aligned with bone regeneration processes. This
defects necessitate clinical intervention. Ideal mandibular adaptability ensures seamless integration with existing
7
reconstruction requires both morphological continuity and bone while providing stable mechanical support.
functional rehabilitation. At present, vascularized bone Furthermore, their tunable mechanical properties allow
grafts remain one of the optimal approaches for mandibular customization of stiffness and degradation rates to meet
defect repair and quality-of-life improvement. Vascularized mandibular reconstruction requirements. Taking gelatin
fibula flaps with over 95% success rates are considered methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogel as an example, due to its
the gold standard for jaw reconstruction. Nevertheless, excellent biocompatibility, tunable mechanical properties,
3
complications such as donor site infections, chronic pain, and potential for functionalization, it has shown great
and poor osseointegration continue to constrain clinical applications in the repair of different types of bone defects.
outcomes. Thus, there is a pressing clinical demand for When combined with other bioactive materials, they offer
the innovative development of bioactive materials as highly customized and effective treatment strategies for
alternatives that can precisely fill bone defects, as well as bone tissue regeneration, meeting the needs for treating
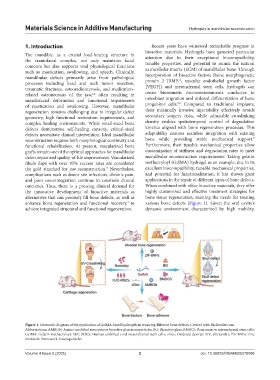
enhance bone regeneration and functional recovery, to various bone defects (Figure 1). Given the oral cavity’s
4
achieve integrated structural and functional regeneration. dynamic environment characterized by high mobility,
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the application of GelMA-based hydrogels in repairing different bone defects. Created with BioRender.com
Abbreviations: AMBGN: Amino-modified mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles; BG: Bioactive glass; BMSCS: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells;
GelMA: Gelatin methacryloyl; hUC-MSCs: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; oDex: Oxidized dextran; UV: Ultraviolet; ZIF-8NPs: Zinc
imidazole framework-8 nanoparticles
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 2 doi: 10.36922/MSAM025070006