Page 20 - MSAM-4-2
P. 20
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Hydrogels in mandibular reconstruction
A B C
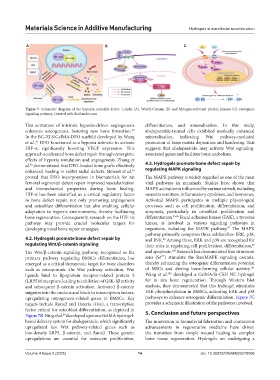
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (A), Wnt/β-Catenin (B) and Mitogen-activated protein kinases (C) osteogenic
signaling pathway. Created with BioRender.com
This activation of intrinsic hypoxia-driven angiogenesis differentiation, and mineralization. In this study,
enhances osteogenesis, fostering new bone formation. abaloparatide-treated cells exhibited markedly enhanced
90
In the BG-XLS/GelMA-DFO scaffold developed by Wang mineralization, indicating Wnt pathway-mediated
et al., DFO functioned as a hypoxia mimetic to activate promotion of bone matrix deposition and hardening. This
91
HIF-α, significantly boosting VEGF expression. This suggests that abaloparatide may activate Wnt signaling-
approach accelerated bone defect repair through synergistic associated genes and facilitate bone anabolism.
effects of hypoxia simulation and angiogenesis. Zhang et
al. demonstrated that DFO-loaded bone grafts effectively 4.3. Hydrogels promote bone defect repair by
92
enhanced healing in rabbit radial defects. Stewart et al. regulating MAPK signaling
93
proved that DFO incorporation in biomaterials for rat The MAPK pathway is widely regarded as one of the most
femoral segmental defect repair improved vascularization vital pathways in mammals. Studies have shown that
and biomechanical properties during bone healing. MAPK activation is influenced by various stimuli, including
HIF-α has been identified as a critical regulatory factor neurotransmitters, inflammatory cytokines, and hormones.
in bone defect repair, not only promoting angiogenesis Activated MAPK participates in multiple physiological
and osteoblast differentiation but also enabling cellular processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and
adaptation to hypoxic environments, thereby facilitating apoptosis, particularly in osteoblast proliferation and
bone regeneration. Consequently, research on the HIF-1α differentiation. 95,96 Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a tyrosine
pathway may provide crucial molecular targets for kinase, is involved in various signaling pathways in
developing novel bone repair strategies. organisms, including the MAPK pathway. The MAPK
97
pathway primarily comprises three subfamilies: ERK, p38,
4.2. Hydrogels promote bone defect repair by and JNK. Among these, ERK and p38 are recognized for
98
regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling their roles in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation,
99
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, recognized as the and apoptosis. Research has demonstrated that strontium
100
primary pathway regulating BMSCs differentiation, has ions (Sr²⁺) stimulate the Ras/MAPK signaling cascade,
emerged as a critical therapeutic target for bone disorders thereby enhancing the osteogenic differentiation potential
101
such as osteoporosis. On Wnt pathway activation, Wnt of MSCs and driving bone-forming cellular activity.
102
ligands bind to lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 Wang et al. developed a GelMA/Sr-CSH NC hydrogel
(LRP5)/6 receptors, leading to inhibition of GSK-3β activity for in situ bone regeneration. Through Western blot
and subsequent β-catenin activation. Activated β-catenin analysis, they demonstrated that this hydrogel stimulates
migrates into the nucleus and binds to transcription factors, FAK phosphorylation in BMSCs, activating ERK and p38
upregulating osteogenesis-related genes in BMSCs. Key pathways to enhance osteogenic differentiation. Figure 7C
targets include Runx2 and Osterix (Osx), a transcription provides a schematic illustration of the pathways involved.
factor critical for osteoblast differentiation, as depicted in 5. Conclusion and future perspectives
Figure 7B. Ning et al. developed a porous GelMA hydrogel-
94
based delivery system for abaloparatide, which significantly The innovation in biomaterial fabrication and continuous
upregulated key Wnt pathway-related genes such as advancements in regenerative medicine have driven
low-density LRP5, β-catenin, and Runx2. These genetic the transition from simple wound healing to complex
upregulations are essential for osteocyte proliferation, bone tissue regeneration. Hydrogels are undergoing a
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/MSAM025070006