Page 24 - OR-1-2
P. 24
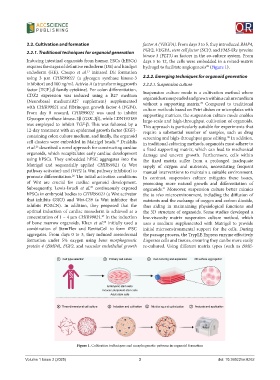
2.2. Cultivation and formation factor A (VEGFA). From days 3 to 5, they introduced BMP4,
FGF2, VEGFA, stem cell factor (SCF), and FMS-like tyrosine
2.2.1. Traditional techniques for organoid generation
kinase 3 (FLT3) as factors in the co-culture system. From
Inducing intestinal organoids from human ESCs (hESCs) days 5 to 12, the cells were embedded in a mixed-matrix
requires the stages of definitive endoderm (DE) and hindgut hydrogel to facilitate angiogenesis (Figure 1).
28
endoderm (HE). Crespo et al. initiated DE formation
13
using 3 μm CHIR99021 (a glycogen synthase kinase-3 2.2.2. Emerging techniques for organoid generation
inhibitor) and 100 ng/mL Activin A (a transforming growth 2.2.2.1. Suspension culture
factor [TGF]-β family cytokine). For colon differentiation, Suspension culture mode is a cultivation method where
CDX2 expression was induced using a B27 medium organoids are suspended and grown within a culture medium
(Neurobasal medium/B27 supplement) supplemented without a supporting matrix. Compared to traditional
29
with CHIR99021 and Fibrinogen growth factor 4 (FGF4). culture methods based on Petri dishes or microplates with
From day 8 onward, CHIR99021 was used to inhibit supporting matrices, the suspension culture mode enables
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), while LDN193189 large-scale and high-throughput cultivation of organoids.
was employed to inhibit TGF-β. This was followed by a This approach is particularly suitable for experiments that
12-day treatment with an epidermal growth factor (EGF)- require a substantial number of samples, such as drug
containing colon culture medium, and finally, the organoid screening and high-throughput gene editing. In addition,
30
cell clusters were embedded in Matrigel beads. Drakhlis in traditional culturing methods, organoids must adhere to
13
et al. described a novel approach for constructing cardiac a fixed supporting matrix, which can lead to mechanical
26
organoids, which recapitulates early cardiac development damage and uneven growth. Furthermore, cells within
using hPSCs. They embedded hPSC aggregates into the the fixed matrix suffer from a prolonged inadequate
Matrigel and sequentially applied CHIR99021 (a Wnt supply of oxygen and nutrients, necessitating frequent
pathway activator) and IWP2 (a Wnt pathway inhibitor) to manual interventions to maintain a suitable environment.
promote differentiation. The initial activation conditions In contrast, suspension culture mitigates these issues,
26
of Wnt are crucial for cardiac organoid development. promoting more natural growth and differentiation of
Subsequently, Lewis-Israeli et al. continuously exposed organoids. Moreover, suspension culture better mimics
27
31
hPSCs in embryoid bodies to CHIR99021 (a Wnt activator the in vivo microenvironment, including the diffusion of
that inhibits GSK3) and Wnt-C59 (a Wnt inhibitor that nutrients and the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide,
inhibits PORCN). In addition, they proposed that the thus aiding in maintaining physiological functions and
optimal induction of cardiac mesoderm is achieved at a the 3D structure of organoids. Some studies developed a
concentration of 1 – 4 μm CHIR99021. In the induction low-viscosity matrix suspension culture method, which
27
of bone marrow organoids, Khan et al. initially used a uses a medium supplemented with Matrigel to provide
28
combination of StemFlex and RevitaCell to form iPSC initial microenvironmental support for the cells. During
aggregates. From days 0 to 3, they induced mesodermal the passage process, the TrypLE Express enzyme effectively
formation under 5% oxygen using bone morphogenetic disperses cells and tissues, ensuring they can be more easily
protein 4 (BMP4), FGF2, and vascular endothelial growth re-cultured. Using different matrix types (such as BME-
Figure 1. Cultivation techniques and morphogenetic patterns in organoid formation
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/or.8262