Page 29 - TD-2-1
P. 29
Tumor Discovery An approach for classification of lung nodules
In this work, we proposed efficient method for
segmentation and classification of lung nodules.
3. Geometric features
Geometric features are considered the first set of features.
The vital structural information of tumor can be easily
analyzed with the 2D and 3D geometric features. The
evaluation of the geometric features is very useful in
quantifying and analyzing the biomedical images like CT
scans (2D, 3D) .
[45]
Image object is formed by the numerous pixels and is
rescaled using unit information. The one unit is the area of
the single pixel, which denotes that the number of pixels
forming the image is the area of the image. If we have the
unit information of the image data provided, then the
area of the whole image is equal to the product of the area
covered by one pixel and the number of pixels unit in the
image object. In this chapter, a fully automatic method is
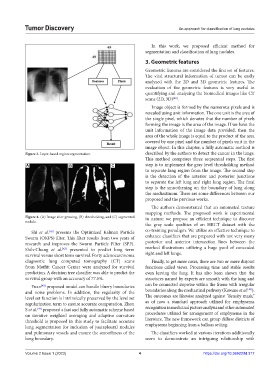
Figure 3. Layer-based region segmentation. described by the authors to detect the cancer in the lungs.
This method comprises three sequential steps. The first
A B C step is to implement the gray level thresholding method
to separate lung region from the image. The second step
is the detection of the anterior and posterior junctions
to separate the left lung and right lung region. The final
step is the smoothening on the boundary of lung along
the mediastinum. There are some differences between our
proposed and the previous works.
The authors demonstrated that an automated texture
mapping methods. The proposed work is experimental
Figure 4. (A) Image after growing, (B) thresholding, and (C) segmented in nature: we propose an efficient technique to discover
nodule.
the gray scale qualities of an HRCT dataset with the
Shi et al. presents the Optimized Kalman Particle co-training paradigm. We utilize an effective technique to
[41]
Swarm (OKPS) filter. This filter results from two years of enhance classifiers that are prepared with not very many
research and improves the Swarm Particle Filter (SPF). posterior and anterior intersection lines between the
Shih-Chung et al. presented to predict long term marked illustrations utilizing a huge pool of concealed
[42]
survival versus short term survival. Forty adenocarcinoma right and left lungs.
diagnostic lung computed tomography (CT) scans Finally, to get more cases, there are two or more disjoint
from Moffitt Cancer Center were analyzed for survival functions called views. Processing time and stable results
prediction. A decision tree classifier was able to predict the even leaving the lung. It has also been shown that the
survival group with an accuracy of 77.5%. structures named by experts are smooth with the lung and
Yuan proposed model can handle blurry boundaries can be connected stepwise within the frame with irregular
[43]
[46]
and noise problems. In addition, the regularity of the boundaries along the mediastinal pathway (Kawane et al. ).
level set function is intrinsically preserved by the level set The outcomes are likewise analyzed against “density mask,”
regularization term to ensure accurate computation. Zhou as of now a standard approach utilized for emphysema
[44]
S et al. proposed a fast and fully automatic scheme based recognition in medicinal picture analysis and other automated
on iterative weighted averaging and adaptive curvature procedures utilized for arrangement of emphysema in the
threshold is proposed in this study to facilitate accurate literature. The new framework can group diffuse districts of
lung segmentation for inclusion of juxtapleural nodules emphysema beginning from a bullous setting.
and pulmonary vessels and ensure the smoothness of the The classifiers worked at various iterations additionally
lung boundary. seem to demonstrate an intriguing relationship with
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.317