Page 57 - TD-3-2
P. 57
Tumor Discovery High-grade sinonasal adenocarcinoma
A B
Figure 2. Characteristic histopathologic features of adenosquamous
carcinoma. (A) Infiltrative pattern of neoplastic nests, dermal
fibrosis/sclerosis, elastosis, and focal ulceration (denoted by asterisk)
(hematoxylin-eosin staining; magnification ×40. (B) Keratinizing cysts
(denoted by small arrow) and glandular elements (denoted by large
arrow) (hematoxylin-eosin staining; magnification ×200.
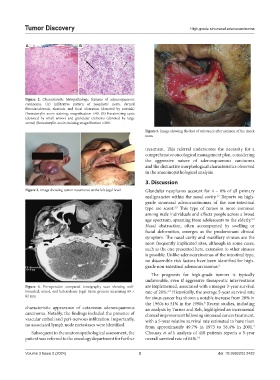
Figure 5. Image showing the loss of substance after excision of the cheek
mass
treatment. This referral underscores the necessity for a
comprehensive oncological management plan, considering
the aggressive nature of adenosquamous carcinoma
and the distinctive morphological characteristics observed
in the anatomopathological analysis.
3. Discussion
Figure 3. Image showing tumor recurrence at the left jugal level Glandular neoplasms account for 4 – 8% of all primary
malignancies within the nasal cavity. Reports on high-
1,2
grade sinonasal adenocarcinomas of the non-intestinal
type are scant. This type of tumor is more common
2,9
among male individuals and affects people across a broad
age spectrum, spanning from adolescents to the elderly. 3,4
Nasal obstruction, often accompanied by swelling or
facial deformities, emerges as the predominant clinical
symptom. The nasal cavity and maxillary sinuses are the
most frequently implicated sites, although in some cases,
such as the one presented here, extension to other sinuses
is possible. Unlike adenocarcinomas of the intestinal type,
no discernible risk factors have been identified for high-
grade non-intestinal adenocarcinomas. 5
The prognosis for high-grade tumors is typically
unfavorable, even if aggressive therapeutic interventions
Figure 4. Pre-operative compared tomography scan showing well- are implemented, associated with a meager 3-year survival
bounded, round, and heterodense jugal tissue process measuring 69 × rate of 20%. Historically, the average 5-year survival rate
6,7
62 mm for sinus cancer has shown a notable increase from 28% in
the 1960s to 51% in the 1990s. Recent studies, including
8
characteristic appearance of cutaneous adenosquamous an analysis by Turner and Reh, highlighted an incremental
carcinoma. Notably, the findings included the presence of clinical improvement following sinonasal cancer treatment,
vascular emboli and peri-nervous infiltration. Importantly, with a 5-year relative survival rate estimated to have risen
no associated lymph node metastases were identified. from approximately 49.7% in 1973 to 56.4% in 2001.
4
Subsequent to the anatomopathological assessment, the Choussy et al.’s analysis of 418 patients reports a 5-year
patient was referred to the oncology department for further overall survival rate of 64%. 10
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/td.2423