Page 101 - TD-3-4
P. 101
Tumor Discovery Bioinformatics insights into CCL2 mutations
I-TASSER server was used to generate a structural approximately −6.3 kcal/mol for the interaction between
model incorporating the specified missense mutation BA and human CCL2, indicates the formation of a favorable
in CCL2. The model underwent molecular dynamics and stable ligand–receptor complex. Understanding these
3
29
(MD) simulations and three-dimensional (3D) modeling molecular interactions through docking studies provides
through WebGro to evaluate how the mutation affected the valuable insights into drug design. By targeting the CCL2–
stability and functionality of the CCL2 protein. WebGro CCR2 interaction, researchers can develop antagonists
30
software was then used to perform MD simulations on that disrupt this pathway. These antagonists hold promise
the mutant CCL2 model, enabling the assessment of its as therapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory
stability and potential functional consequences compared and autoimmune diseases as well as certain cancers where
to the native protein. A thorough analysis of the impact CCL2/CCR2 signaling plays an important role.
of the missense mutation on the protein structure and CCL2 mutations can substantially alter the protein’s
function was facilitated by this integrated computational
approach that combines structure prediction with MD structure and function and potentially affect its
31
(Figure 1). binding affinity to the CCR2 receptor. This may impact
the recruitment and activation of tumor-associated
Molecular docking studies offer valuable insights into macrophages, thereby influencing angiogenesis and
the binding dynamics and interactions between CCL2 tumor progression. This mutation could also modulate
and CCR2, highlighting the potential for therapeutic the immune response to CCL2, potentially influencing
interventions in diseases mediated by this signaling antitumor immunity and macrophage tumoricidal activity.
pathway. Molecular docking analyses have identified the Overall, CCL2 mutations could have profound implications
critical residues in CCL2, such as T16, N17, and R18, which for the tumorigenic potential of this chemokine in cancer
are essential for forming stable complexes with CCR2. development. However, further research is required to
These interactions involve both hydrophobic interactions elucidate the specific genetic and epigenetic factors that
and hydrogen bonds, which collectively contribute to the influence the expression and activity of CCL2 mutations.
binding affinity of CCL2 (ligand) with CCR2 (receptor).
3
For instance, the binding of the compound baicalin (BA) to 2. Material and methods
CCL2 is facilitated by substantial hydrophobic interactions
with residues such as I20 and V51 and hydrogen bonds 2.1. Collection of datasets
with residues such as T16 and S17. The binding energy In this study, we collected data on CCL2 missense mutations
calculated for CCL2 interactions with CCR2, that is, from the Ensembl database (release 109) (https://www.
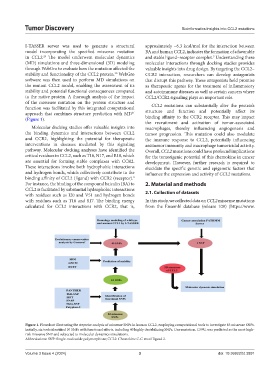
Figure 1. Flowchart illustrating the stepwise analysis of missense SNPs in human CCL2, employing computational tools to investigate 83 missense SNPs.
Initially, six tools identified 10 SNPs with functional effects, including 40 highly destabilizing SNPs. One mutation, C59G, was predicted as the most high-
risk missense SNP and subjected to molecular dynamics simulations.
Abbreviations: SNP: Single-nucleotide polymorphism; CCL2: Chemokine C-C motif ligand 2.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/td.3891