Page 117 - TD-3-4
P. 117
Tumor Discovery Bioinformatics insights into CCL2 mutations
A
B
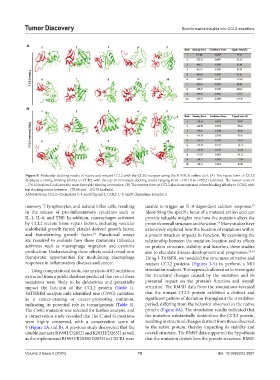
Figure 9. Molecular docking results of native and mutant CCL2 with the CCR2 receptor using the HDOCK online tool. (A) The native form of CCL2
displayed a strong binding affinity to CCR2, with the top 10 minimum docking scores ranging from −176.10 to −150.21 kcal/mol. The lowest score of
−176.10 kcal/mol indicates the most favorable binding interaction. (B) The mutant form of CCL2 also demonstrated robust binding affinity to CCR2, with
top docking scores between −175.86 and −153.79 kcal/mol.
Abbreviations: CCL2: Chemokine C-C motif ligand 2; CCR2: C-C motif chemokine receptor 2.
memory T lymphocytes, and natural killer cells, resulting unable to trigger an IL-8-dependent calcium response.
93
in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as Identifying the specific locus of a mutated amino acid can
IL-1, IL-6, and TNF. In addition, macrophages activated provide valuable insights into how the mutation alters the
by CCL2 secrete tissue repair factors, including vascular protein’s overall structure and function. Many studies have
94
endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, extensively explored how the location of mutations within
and transforming growth factor. Functional assays a protein structure impacts its function. By examining the
92
are required to evaluate how these mutations influence relationship between the mutation location and its effects
activities such as macrophage migration and cytokine on protein structure, stability, and function, these studies
production. Understanding these effects could reveal new aim to elucidate disease development and progression. 95,96
therapeutic opportunities for modulating macrophage Using I-TASSER, we modeled the structures of native and
responses in inflammatory diseases and cancer. mutant CCL2 proteins (Figures 3-5) to perform a MD
Using computational tools, our analysis of 83 mutations simulation analysis. This approach allowed us to investigate
extracted from a public database predicted that ten of these the structural changes caused by the mutation and its
mutations were likely to be deleterious and potentially potential impact on the protein’s function and overall
impact the function of the CCL2 protein (Table 1). structure. The RMSD data from the simulations revealed
FATHMM analysis only identified one (C59G) mutation that the mutant CCL2 protein exhibited a distinct and
as a cancer-causing or cancer-promoting mutation, significant pattern of deviation throughout the simulation
indicating its potential role in tumorigenesis (Table 3). period, differing from the behavior observed in the native
The C59G mutation was selected for further analysis, and protein (Figure 4A). The simulation results indicated that
a conservation study revealed that the C and G positions the mutation substantially destabilizes the CCL2 protein,
were highly conserved, with a conservation score of resulting in structural changes distinct from those observed
9 (Figure 2A and B). A previous study discovered that the in the native protein, thereby impacting its stability and
double mutants R199H/D265H and R203H/D265H as well overall structure. The RMSF data supported the hypothesis
as the triple mutant R199H/R203H/D265H in CXCR1 were that the mutation destabilizes the protein structure. RMSF
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 19 doi: 10.36922/td.3891