Page 146 - TD-3-4
P. 146
Tumor Discovery Primarily enucleated RB patient’s analysis
• Group E: Massive tumor causing anatomical or sclera, extraocular structures, and retrolaminar optic
functional eye destruction, with neovascular nerve (including the cut end). 11,12 Tumor differentiation
glaucoma, intraocular tumor (Figure 1), aseptic orbital was classified according to rosette formation into well-
cellulitis, tumor touching the lens, tumor anterior to differentiated (presence of Homer–Wright, Flexner–
the anterior vitreous face, diffuse infiltrating tumor, Wintersteiner, and/or fleurettes), moderately differentiated
and phthisis or pre-phthisis. (presence of Homer–Wright and/or Flexner–Wintersteiner
The IRSS categorizes patients with RB into five rosettes), poorly differentiated (presence of only Homer–
stages (Stages 0 – IV). Stage 0 includes patients treated Wright rosettes), and undifferentiated (absence of rosettes/
13
conservatively, whereas Stage I includes cases with fleurettes).
enucleated eyes in which resection is histologically This retrospective study posed no risk to individual
complete. Stage II indicates a microscopic residual tumor patient identification; therefore, institutional review board
in an enucleated eye. Stage III includes regional extension, (IRB) approval was obtained. The study was approved
subdivided into overt orbital disease and pre-auricular by the local IRB and conducted in accordance with the
or cervical lymph node involvement. Stage IV involves principles of the 2013 Declaration of Helsinki.
distant metastatic disease and is further divided into two
subgroups: (a) Hematogenous metastasis, with a single 2.3. Statistical analysis
lesion or multiple lesions, and (b) central nervous system Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 16, with
(CNS) extension, with pre-chiasmatic lesions, CNS mass, a P < 0.05 considered statistically significant. Differences
or leptomeningeal disease. between the male and female symptom duration were
Data were collected about age, sex, laterality analyzed using an independent t-test. Survival rates were
of the tumor, presenting symptoms, duration of calculated using Kaplan–Meier survival analysis.
symptoms, tumor grading and staging, tumor growth 3. Results
pattern, tumor differentiation, histopathological HRFs,
adjuvant treatments received, follow-up period, and 3.1. Demographic profile
survival. Of the 96 patients, data from 78 patients were The mean age of the patients was 34.56 ± 19.90 months,
completed and included in the study. Patients who had ranging from 3 months to 90 months. Males had a mean
undergone secondary enucleation or had incomplete data age of 35.90 ± 20.95 months, whereas females had a mean
were excluded from the study. age of 32.91 ± 19.68 months. The overall median age
The criteria for histopathological HRFs were selected was 33 months (30 months for males and 35 months for
based on various global studies conducted to identify and females). The lowest and highest presenting ages in males
evaluate HRFs, including anterior chamber, iris, trabecular were 3 months and 90 months, respectively, whereas those
meshwork, Schlemm’s canal, ciliary body, choroid (massive, in females were 4 months and 84 months, respectively.
defined as >3 mm choroidal invasion in thickness or width), Approximately 62% of the children were older than
24 months, with 31% aged 13–24 months and 8% being
younger than 12 months. The most frequent presenting age
was 24 months.
Male patients accounted for 55.1% (n = 43) of
the included patients, whereas females accounted for
44.9% (n = 35) of the total patients, yielding a male-to-
female ratio of 1.4:1 (Table 1). Approximately 90% of
cases were unilateral RB. Among bilaterally presenting
cases (10.3%, n = 8), only one child underwent bilateral
enucleation (1.3%). Left-eye involvement was more
common (53.6%). Only 2.6% (n = 2) had a family history
of RB, presenting as unilateral cases.
3.2. Lag time with clinical presentation
The mean duration from symptom onset to diagnosis was
5.89 ± 4.30 months (5.68 ± 3.56 months for males and 5.94
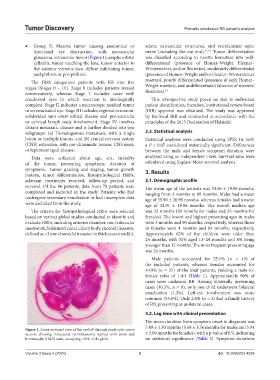
Figure 1. Cross-sectional view of the eyeball through pupil-optic nerve
section, showing intraocular retinoblastoma stained with eosin and ± 5.09 months for females), with a p-value of 0.9, indicating
hematoxylin (H&E) stain, occupying >50% of the globe no statistical significance (Table 2). Symptom durations
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/td.4336