Page 148 - TD-3-4
P. 148
Tumor Discovery Primarily enucleated RB patient’s analysis
3.4. Treatment and outcomes
In addition to primary enucleation, 33.3% (n = 26) of
patients received adjuvant chemotherapy only and 5.1%
(n = 4) received both adjuvant chemotherapy and external
beam radiotherapy (EBRT). A total of 57.7% (n = 45) of
patients underwent primary enucleation without additional
chemotherapy due to the absence of histopathological HRFs
and 3.8% (n = 3) refused further treatment. Approximately
27% (n = 21) of children died and 3.8% (n = 3) were lost
to follow-up (presumed deceased). Approximately 23.07%
(n = 18) of patients died due to metastasis and 3.8% (n = 3)
died suddenly of unknown causes. The overall survival rate
was 69.23%. The follow-up period after enucleation ranged
from 6 months to 12 years.
4. Discussion
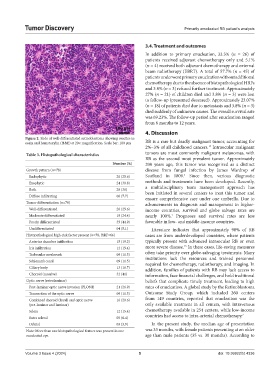
Figure 2. Slide of well-differentiated retinoblastoma showing rosettes in
eosin and hematoxylin (H&E) at 20× magnification. Scale bar: 100 µm RB is a rare but deadly malignant tumor, accounting for
2%–3% of all childhood cancers. Intraocular malignant
14
Table 3. Histopathological characteristics tumors are most commonly malignant melanomas, with
RB as the second most prevalent tumor. Approximately
Number (%) 200 years ago, this tumor was recognized as a distinct
Growth pattern (n=78) disease from fungal infection by James Wardrop of
1
Endophytic 20 (25.6) Scotland in 1809. Since then, various diagnostic
Exophytic 24 (30.8) methods and treatments have been developed. Recently,
Both 28 (36) a multidisciplinary team management approach has
been initiated in several centers to treat this tumor and
Diffuse infiltrating 06 (7.7) ensure comprehensive care under one umbrella. Due to
Tumor differentiation (n=78) advancements in diagnosis and management in higher-
Well-differentiated 20 (25.6) income countries, survival and globe salvage rates are
Moderate differentiated 19 (24.4) nearly 100%. Prognoses and survival rates are less
7
Poorly differentiated 35 (44.9) favorable in low- and middle-income countries.
Undifferentiated 04 (5.1) Literature indicates that approximately 90% of RB
Histopathological high-risk factor present (n=78, HRF=66) cases are from underdeveloped countries, where patients
Anterior chamber infiltration 15 (19.2) typically present with advanced intraocular RB or even
15
Iris infiltration 12 (15.4) more severe disease. In these cases, life-saving measures
Trabecular meshwork 09 (11.5) often take priority over globe-salvaging treatments. Many
Schlemm’s canal 09 (11.5) institutions lack the resources and trained personnel
required for chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and imaging. In
Ciliary body 13 (16.7) addition, families of patients with RB may lack access to
Choroid (massive) 32 (41) information, face financial challenges, and hold traditional
Optic nerve (retrolaminar) beliefs that complicate timely treatment, leading to high
Post-laminar optic nerve invasion (PLONI) 21 (26.9) rates of enucleation. A global study by the Retinoblastoma
Transection of the optic nerve 09 (11.5) Outcome Study Group, which included 260 centers
Combined choroid (focal) and optic nerve 16 (20.6) from 149 countries, reported that enucleation was the
(pre-laminar and laminar) only available treatment in all centers, with intravenous
Sclera 12 (15.4) chemotherapy available in 254 centers, while low-income
Extra scleral 05 (6.4) countries had access to intra-arterial chemotherapy. 7
Orbital 03 (3.9) In the present study, the median age of presentation
Note: More than one histopathological feature was present in one was 33 months, with female patients presenting at an older
enucleated eye. age than male patients (35 vs. 30 months). According to
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/td.4336