Page 171 - TD-3-4
P. 171
Tumor Discovery Signet ring cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder
A D E
B
C
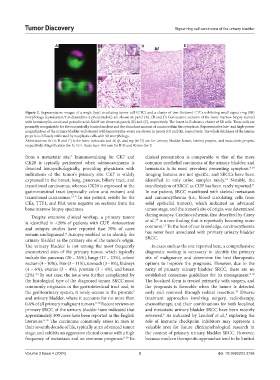
Figure 2. Representative images of a single (top) circulating tumor cell (CTC) and a cluster of two (bottom) CTCs exhibiting small signet ring (SR)
morphology (cytokeratin/4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) are shown in panel (A). (B and C) Consecutive sections of the bone marrow biopsy stained
with hematoxylin–eosin and periodic acid–Schiff are shown in panels (B) and (C), respectively. The insert in B shows a cluster of SR cells. These cells are
promptly recognizable for the eccentrically located nucleus and the abundant amount of mucin within the cytoplasm. Representative low- and high-power
magnification of the urinary bladder wall stained with hematoxylin–eosin are shown in panels (D) and (E), respectively. The whole thickness of the lamina
propria is diffusely infiltrated by neoplastic cells with SR morphology.
Abbreviations: bt (in B and C) is for bone trabecula and bl, lp, and mp (in D) are for urinary bladder lumen, lamina propria, and muscularis propria,
respectively. Magnification for A: 10 ×. Scale bars: 100 mm for B-D and 80 mm for E.
from a metastatic site. Immunostaining for CK7 and clinical presentation is comparable to that of the more
3
CK20 is typically performed when adenocarcinoma is common urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder, and
detected histopathologically, providing physicians with hematuria is its most prevalent presenting symptom. 8-10
indications of the tumor’s primary site. CK7 is widely Imaging features are not specific, and SRCCs have been
expressed in the breast, lung, pancreas, biliary tract, and identified in only urine samples rarely. Notably, the
13
transitional carcinomas, whereas CK20 is expressed in the manifestation of SRCC as CUP has been rarely reported.
11
gastrointestinal tract (especially colon and rectum) and In our patient, SRCC manifested with skeletal metastasis
transitional carcinomas. 1,3-6 In our patient, results for the and carcinocythemia (i.e., blood circulating cells from
CKs, TTF1, and PSA were negative on sections from the solid epithelial tumors), which indicated an advanced
bone marrow biopsy specimen. tumor stage, and the tumor’s site of origin was determined
Despite extensive clinical workup, a primary tumor during autopsy. Carcinocythemia, first described by Carey
14
is identified in <20% of patients with CUP. Antemortem et al., is a rare finding that is reportedly becoming more
15
and autopsy studies have reported that 70% of cases common. To the best of our knowledge, carcinocythemia
4
remain undiagnosed. Autopsy enabled us to identify the has never been associated with primary urinary bladder
urinary bladder as the primary site of the tumor’s origin. SRCC.
The urinary bladder is not among the most frequently In cases such as the one reported here, a comprehensive
encountered sites of the primary tumor, which typically diagnostic workup is necessary to identify the primary
include the pancreas (20 – 26%), lungs (17 – 23%), colon/ site of malignancy and determine the best therapeutic
rectum (4 – 10%), liver (3 – 11%), stomach (3 – 8%), kidneys options to improve the prognosis. However, due to the
(4 – 6%), ovaries (3 – 4%), prostate (3 – 4%), and breast rarity of primary urinary bladder SRCC, there are no
(2%). In our case, the issue was further complicated by established consensus guidelines for its management. 8-10
3,4
the histological type of the diagnosed tumor. SRCC most The localized form is treated primarily with surgery, and
commonly originates in the gastrointestinal tract and, in the prognosis is favorable when the tumor is detected
the genitourinary system, it rarely occurs in the prostate early and removed through radical resection. Diverse
7
10
and urinary bladder, where it accounts for no more than treatment approaches involving surgery, radiotherapy,
0.6% of all primary malignant tumors. 8-10 Recent reviews on chemotherapy, and their combinations for both localized
primary SRCC of the urinary bladder have indicated that and metastatic urinary bladder SRCC have been recently
approximately 300 cases have been reported in the English reviewed. As indicated by Lendorf et al., exploring the
8
8
literature. 8-10 The carcinoma commonly arises in men in role of immune checkpoint inhibitors may represent a
their seventh decade of life, typically at an advanced tumor valuable area for future clinicopathological research in
stage, and exhibits an aggressive clinical course with a high the context of primary urinary bladder SRCC. However,
frequency of metastasis and an ominous prognosis. 8-10 Its because modern therapeutic approaches tend to be limited
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/td.3736