Page 175 - TD-3-4
P. 175
Tumor Discovery Sarcomatoid mesothelioma: A case report
2. Case presentation
A 50-year-old female with diabetes presented with acute-
on-chronic right-sided upper back pain. Nine months
before presentation, the patient experienced intermittent
right-sided back pain without an identifiable trigger.
Subsequently, non-productive cough and dyspnea on
exertion developed 4 months before presentation. Her
symptoms progressed, and she developed progressively
worsening anorexia and nausea, as well as experiencing
20 pounds of unintentional weight loss over 2 weeks, all
of which prompted her to seek medical consultation and
her admission to the hospital. Fevers, chills, and chest pain
were absent. She was a non-smoker with no history of
secondhand smoke exposure. According to her, multiple
family members had succumbed to an unknown lung Figure 1. Computed tomography of the thorax in the axial plane shows
cancer. a 14.5 × 6.9 cm mass arising from the mediastinum, which invades the
Physical examination revealed tachycardia and anterior chest wall and causes significant superior vena cava stenosis.
decreased breath sounds over the middle and lower lobes
of the right lung. Routine hematology was notable for mild A B
neutrophilic leukocytosis and thrombocytosis. Additional
metabolic and infectious testing was unrevealing. A chest
radiograph showed a large right-sided pleural effusion
with compressive atelectasis. Computed tomography (CT)
of the chest redemonstrated the effusion and revealed
a 14.5 × 6.9 cm centrally necrotic right hemithorax
mass arising from the mediastinum with invasion into C D
the adjacent anterior chest wall and compression of the
superior vena cava and right interlobar and upper lobe
bronchi (Figure 1).
The patient developed hypoxemia. Subsequently, a
chest tube was placed, and cytologic examination revealed
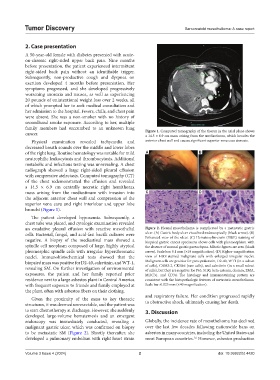
an exudative pleural effusion with reactive mesothelial Figure 2. Pleural mesothelioma is complicated by a metastatic gastric
cells. Bacterial, fungal, and acid-fast bacilli cultures were ulcer. (A) Gastric body ulcer visualized endoscopically (black arrow). (B)
Enhanced view of the ulcer. (C) Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining of
negative. A biopsy of the mediastinal mass showed a biopsied gastric cancer specimens shows cells with pleomorphism with
spindle cell neoplasm composed of large, highly atypical the absence of normal gastric parenchyma. Mitotic figures are seen (black
pleomorphic spindle cells with irregular hyperchromatic arrow). Scale bar: 0.1 mm (×10 magnification). (D) Higher-magnification
nuclei. Immunohistochemical tests showed that the view of H&E-stained malignant cells with enlarged irregular nuclei.
biopsied mass was positive for D2-40, calretinin, and WT-1, Malignant cells are positive for pancytokeratin, D2-40, WT1 (in a subset
of cells), CAM5.2, CK5&6 (rare cells), and calretinin (in a small subset
revealing SM. On further investigation of environmental of cells), but they are negative for P63, S100, beta-catenin, desmin, EMA,
exposures, the patient and her family reported prior MOC31, and CD34. The histology and immunostaining pattern are
residence next to a large asbestos plant in Central America consistent with the histopathologic features of metastatic mesothelioma.
with frequent exposure to friends and family employed at Scale bar: 0.025 mm (×40 magnification).
the plant, often with asbestos fibers on their clothing.
and respiratory failure. Her condition progressed rapidly
Given the proximity of the mass to key thoracic
structures, it was deemed unresectable, and the patient was to obstructive shock, ultimately causing her death.
to start chemotherapy at discharge. However, she suddenly 3. Discussion
developed large-volume hematemesis and an emergent
endoscopy was immediately conducted, revealing a Globally, the incidence rate of mesothelioma has declined
malignant gastric ulcer, which was confirmed on biopsy over the last few decades following nationwide bans on
to be metastatic SM (Figure 2). Shortly thereafter, she asbestos in many countries, including the United States and
developed a pulmonary embolism with right heart strain most European countries. However, asbestos production
1,6
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/td.4420