Page 83 - TD-4-1
P. 83
Tumor Discovery Colorectal cancer: miRNA, mRNA, protein insights
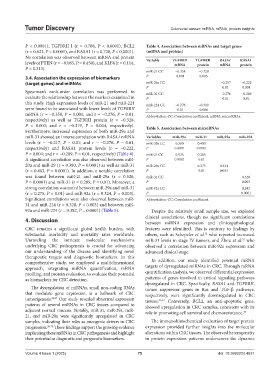
P < 0.0001), TGFBRII I (r = 0.708, P < 0.0001), BCL2 Table 4. Association between mRNAs and target genes
(r = 0.623, P < 0.0001), and RASA1 (r = 0.728, P < 0.0001). (mRNA and protein)
No correlation was observed between mRNA and protein Variable TGFBRII TGFBRII RASA1 RASA1
levels of PTEN (r = −0.085, P = 0.450), and KLF4 (r = 0.114, mRNA protein mRNA protein
P = 0.313).
miR-21 CC −0.358 −0.328
3.4. Association the expression of biomarkers P 0.001 0.003
(target genes) and miRNAs miR-29a CC −0.217 −0.222
P 0.01 0.004
Spearman’s rank-order correlation was performed to miR-31 CC −0.276 −0.209
evaluate the relationship between the markers examined in P 0.01 0.01
this study. High expression levels of miR-21 and miR-224 miR-224 CC −0.276 −0.319
were found to be associated with lower levels of TGFBRII P 0.01 0.004
mRNA (r = −0.358, P = 0.001; and r = −0.276, P = 0.01, Abbreviation: CC: Correlation coefficient; mRNA: microRNAs.
respectively) as well as TGFBRII protein (r = −0.328,
P = 0.003; and r = −0.319, P = 0.004, respectively). Table 5. Association between microRNAs
Furthermore, increased expression of both miR-29a and
miR-31 showed an inverse correlation with RASA1 mRNA Variables miR‑29a miR‑31 miR‑92a miR‑224
levels (r = −0.217, P = 0.01; and r = −0.276, P = 0.01, miR-20a CC 0.380 0.403
respectively) and RASA1 protein levels (r = −0.222, P 0.0001 0.0001
P = 0.004; and r = −0.209, P = 0.01, respectively) (Table 4). miR-21 CC 0.526 0.285
A significant correlation was also observed between miR- P 0.0001 0.01
20a and miR-29 (r = 0.380, P = 0.0001) as well as miR-31 miR-29a CC 0.275 0.324
(r = 0.403, P = 0.0001). In addition, a notable correlation P 0.01 0.003
was found between miR-21 and miR-29a (r = 0.526, miR-31 CC 0.328
P = 0.0001) and miR-31 (r = 0.285, P = 0.01). Moreover, a P 0.003
strong correlation was noted between miR-29a and miR-31 miR-92a CC 0.382
(r = 0.275, P = 0.01) and miR-92a (r = 0.324, P = 0.003). P 0.0001
Significant correlations were also observed between miR- Abbreviation: CC: Correlation coefficient.
31 and miR-224 (r = 0.328, P = 0.003) and between miR-
92a and miR-224 (r = 0.382, P = 0.0001) (Table 5). Despite the relatively small sample size, we explored
clinical associations, though no significant correlations
4. Discussion between miRNA expression and clinicopathological
CRC remains a significant global health burden, with features were identified. This is contrary to findings by
substantial morbidity and mortality rates worldwide. others, such as Schepeler et al. who reported increased
31
Unraveling the intricate molecular mechanisms miR-31 levels in stage IV tumors, and Zhou et al. who
32
underlying CRC pathogenesis is crucial for advancing observed a correlation between miR-92a expression and
our understanding of the disease and identifying novel advanced clinical stage.
therapeutic targets and diagnostic biomarkers. In this In addition, our study identified potential mRNA
comprehensive study, we employed a multidimensional
approach, integrating miRNA quantification, mRNA targets of dysregulated miRNAs in CRC. Through mRNA
profiling, and protein evaluation, to evaluate their potential quantification analysis, we observed differential expression
as biomarkers for CRC detection. patterns of genes involved in critical signaling pathways
dysregulated in CRC. Specifically, RASA1 and TGFBRII,
The dysregulation of miRNAs, small non-coding RNAs tumor suppressor genes in Ras and TGF-β pathways,
that modulate gene expression, is a hallmark of CRC respectively, were significantly downregulated in CRC
tumorigenesis. 26,27 Our study revealed abnormal expression tissues. 33,34 Conversely, BCL2, an anti-apoptotic gene,
patterns of several miRNAs in CRC tissues compared to showed upregulation in CRC samples, consistent with its
adjacent normal mucosa. Notably, miR-31, miR-29a, miR- role in promoting cell survival and chemoresistance. 35
21, and miR-20a were significantly upregulated in CRC
samples, indicating their roles as oncogenic drivers in CRC The immunohistochemical evaluation of target protein
progression. 28-30 These findings support the growing evidence expression provided further insights into the molecular
implicating these miRNAs in CRC pathogenesis and highlight alterations within CRC tissues. The observed heterogeneity
their potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. in protein expression patterns underscores the dynamic
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 75 doi: 10.36922/td.4631