Page 11 - TD-4-3
P. 11
Tumor Discovery FBXW7 in Leukemia
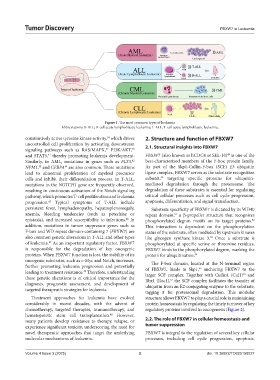
Figure 1. The most common types of leukemia
Abbreviations: B-ALL; B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; T-ALL: T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
constitutively active tyrosine kinase activity, which drives 2. Structure and function of FBXW7
38
uncontrolled cell proliferation by activating downstream
signaling pathways such as RAS/MAPK, PI3K/AKT, 2.1. Structural insights into FBXW7
39
40
and STAT5, thereby promoting leukemia development. FBXW7 (also known as hCDC4 or SEL-10) is one of the
49
41
Similarly, in AML, mutations in genes such as FLT3, best-characterized members of the F-box protein family.
42
NPM1, and CEBPA are also common. These mutations As part of the Skp1-Cullin-F-box (SCF) E3 ubiquitin
43
44
lead to abnormal proliferation of myeloid precursor ligase complex, FBXW7 serves as the substrate recognition
50
cells and inhibit their differentiation process. In T-ALL, subunit, targeting specific proteins for ubiquitin-
mutations in the NOTCH1 gene are frequently observed, mediated degradation through the proteasome. The
resulting in continuous activation of the Notch signaling degradation of these substrates is essential for regulating
pathway, which promotes T-cell proliferation and leukemia critical cellular processes such as cell cycle progression,
progression. Typical symptoms of T-ALL include apoptosis, differentiation, and signal transduction.
45
persistent fever, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, Substrate specificity of FBXW7 is dictated by its WD40
anemia, bleeding tendencies (such as petechiae or repeat domain, a β-propeller structure that recognizes
51
epistaxis), and increased susceptibility to infections. In phosphorylated degron motifs on its target proteins.
46
52
addition, mutations in tumor suppressor genes such as This interaction is dependent on the phosphorylation
F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7 (FBXW7) are status of the substrate, often mediated by upstream kinases
also common genetic alterations in T-ALL and other types like glycogen synthase kinase 3. Once a substrate is
53
of leukemia. As an important regulatory factor, FBXW7 phosphorylated at specific serine or threonine residues,
47
is responsible for the degradation of key oncogenic FBXW7 binds to the phosphorylated degron, marking the
proteins. When FBXW7 function is lost, the stability of its protein for ubiquitination. 54
oncogenic substrates, such as c-Myc and Notch, increases, The F-box domain, located at the N-terminal region
further promoting leukemia progression and potentially of FBXW7, binds to Skp1, anchoring FBXW7 to the
55
leading to treatment resistance. Therefore, understanding larger SCF complex. Together with Cullin1 (Cul1) and
48
56
these genetic alterations is of critical importance for the Rbx1 (Roc1), the SCF complex facilitates the transfer of
57
diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and development of ubiquitin from an E2-conjugating enzyme to the substrate,
targeted therapeutic strategies for leukemia. tagging it for proteasomal degradation. This modular
Treatment approaches for leukemia have evolved structure allows FBXW7 to play a crucial role in maintaining
considerably in recent decades, with the advent of protein homeostasis by regulating the timely turnover of key
chemotherapy, targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and regulatory proteins involved in oncogenesis (Figure 2).
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. However,
48
many patients develop resistance to therapy, relapse, or 2.2. The role of FBXW7 in cellular homeostasis and
experience significant toxicity, underscoring the need for tumor suppression
novel therapeutic approaches that target the underlying FBXW7 is integral to the regulation of several key cellular
molecular mechanisms of leukemia. processes, including cell cycle progression, apoptosis,
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/TD025150027