Page 15 - TD-4-3
P. 15
Tumor Discovery FBXW7 in Leukemia
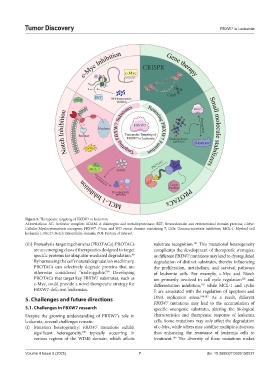
Figure 5. Therapeutic targeting of FBXW7 in leukemia
Abbreviations: AC: Activator complex; ADAM: A disintegrin and metalloproteinase; BET: Bromodomain and extraterminal domain proteins; c-Myc:
Cellular Myelocytomatosis oncogene; FBXW7: F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7; GSIs: Gamma-secretase inhibitors; MCL-1: Myeloid cell
leukemia 1; NICD: Notch intracellular domain; POI: Protein of interest.
(iii) Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs): PROTACs substrate recognition. This mutational heterogeneity
101
are an emerging class of therapeutics designed to target complicates the development of therapeutic strategies,
specific proteins for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. as different FBXW7 mutations may lead to dysregulated
98
By harnessing the cell’s natural degradation machinery, degradation of distinct substrates, thereby influencing
PROTACs can selectively degrade proteins that are the proliferation, metabolism, and survival pathways
otherwise considered “undruggable.” Developing of leukemia cells. For example, c-Myc and Notch
99
PROTACs that target key FBXW7 substrates, such as are primarily involved in cell cycle regulation and
102
c-Myc, could provide a novel therapeutic strategy for differentiation inhibition, while MCL-1 and cyclin
103
FBXW7-deficient leukemias. E are associated with the regulation of apoptosis and
5. Challenges and future directions DNA replication stress. 104,105 As a result, different
FBXW7 mutations may lead to the accumulation of
5.1. Challenges in FBXW7 research specific oncogenic substrates, altering the biological
Despite the growing understanding of FBXW7’s role in characteristics and therapeutic response of leukemia
leukemia, several challenges remain: cells. Some mutations may only affect the degradation
(i) Mutation heterogeneity: FBXW7 mutations exhibit of c-Myc, while others may stabilize multiple substrates,
significant heterogeneity, typically occurring in thus enhancing the resistance of leukemia cells to
100
various regions of the WD40 domain, which affects treatment. The diversity of these mutations makes
106
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/TD025150027