Page 13 - TD-4-3
P. 13
Tumor Discovery FBXW7 in Leukemia
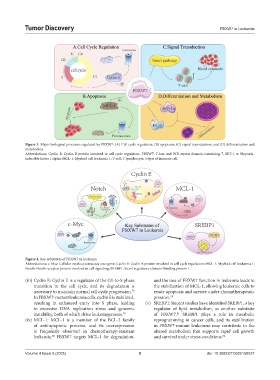
Figure 3. Major biological processes regulated by FBXW7. (A) Cell cycle regulation; (B) apoptosis; (C) signal transduction; and (D) differentiation and
metabolism.
Abbreviations: Cyclin E: Cyclin E protein involved in cell cycle regulation; FBXW7: F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7; HIF-1 α: Hypoxia-
inducible factor 1 alpha; MCL-1: Myeloid cell leukemia 1; T-cell: T lymphocyte, a type of immune cell.
Figure 4. Key substrates of FBXW7 in leukemia
Abbreviations: c-Myc: Cellular myelocytomatosis oncogene; Cyclin E: Cyclin E protein involved in cell cycle regulation; MCL-1: Myeloid cell leukemia 1;
Notch: Notch receptor protein involved in cell signaling; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1.
(iii) Cyclin E: Cyclin E is a regulator of the G1-to-S phase and the loss of FBXW7 function in leukemia leads to
transition in the cell cycle, and its degradation is the stabilization of MCL-1, allowing leukemic cells to
necessary to maintain normal cell cycle progression. evade apoptosis and survive under chemotherapeutic
78
In FBXW7-mutant leukemia cells, cyclin E is stabilized, pressure. 50
resulting in enhanced entry into S phase, leading (v) SREBP1: Recent studies have identified SREBP1, a key
to excessive DNA replication stress and genomic regulator of lipid metabolism, as another substrate
instability, both of which drive leukemogenesis. 79 of FBXW7. SREBP1 plays a role in metabolic
81
(iv) MCL-1: MCL-1 is a member of the BCL-2 family reprogramming in cancer cells, and its stabilization
of anti-apoptotic proteins, and its overexpression in FBXW7-mutant leukemias may contribute to the
is frequently observed in chemotherapy-resistant altered metabolism that supports rapid cell growth
leukemia. FBXW7 targets MCL-1 for degradation, and survival under stress conditions. 82
80
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/TD025150027