Page 125 - AIH-1-2
P. 125
Artificial Intelligence in Health SDoH in clinical narratives
models trained in the medical literature. We believe that model 25,30 and produced a list of sentences for every article.
our research adds to the discussion on SDoH, which could Our focus was strictly on sentences that mentioned the
consequently enhance AI tools and policies for unbiased patients’ age and gender and identified using the same set
reporting of these determinants. of regular expressions. These sentences were then input
into a pre-trained named-entity recognition (NER) model
2. Methods from John Snow Labs (JSL), designed to identify mentions
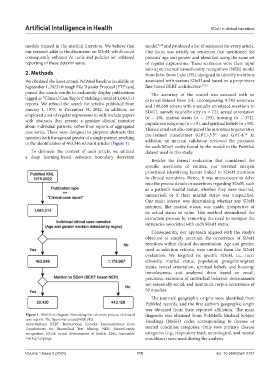
We obtained the latest annual PubMed baseline (available on associated with various SDoH and based on a proprietary
September 1, 2023) through File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and fine-tuned BERT architecture. 31,32
parsed the search results to exclusively display publications The accuracy of the model was assessed with an
tagged as “Clinical Case Report,” yielding a total of 1,643,513 external dataset from JSL, encompassing 9,743 sentences
reports. We refined the search for articles published from and 198,698 tokens with manually annotated mentions to
January 1, 1975, to December 31, 2022. In addition, we SDoH, namely race/ethnicity (n = 72), sexual orientation
employed a set of regular expressions to only include papers (n = 20), marital status (n = 193), housing (n = 371),
with abstracts that present a genuine clinical narrative population subgroup (n = 19), and spiritual beliefs (n = 90).
about individual patients, rather than reports of aggregated This external test also compared the outcomes to generative
case series. These were designed to pinpoint abstracts that pre-trained transformer (GPT)-3.5 and GPT-4. In
34
33
mention both the age and gender of a single patient, resulting addition, an internal validation reviewed the precision
in the identification of 463,546 relevant articles (Figure 1).
for each SDoH entity found by the model in the PubMed
To delineate the content of each article, we utilized dataset used in this study.
a deep learning-based sentence boundary detection
Besides the formal evaluation that considered the
specific assertions of entities, our internal analysis
prioritized identifying factors linked to SDoH mentions
in clinical narratives. Hence, it was unnecessary to delve
into the precise details or assertions regarding SDoH, such
as a patient’s marital status, whether they were married,
unmarried, or if their marital status was unspecified.
Our main interest was determining whether any SDoH
mention, like marital status, was made, irrespective of
its actual status or value. This method streamlined the
extraction process by removing the need to navigate the
intricacies associated with each SDoH status.
Consequently, our approach aligned with the study’s
objective to simply ascertain the occurrence of SDoH
mentions within clinical documentation. Age and gender,
used as selection criteria, were omitted from the SDoH
evaluation. We targeted six specific SDoH, i.e., race/
ethnicity, marital status, population group/immigrant
status, sexual orientation, spiritual beliefs, and housing/
homelessness, and analyzed them based on recall,
precision, exclusion of individual behavior determinants
not essentially social, and minimum corpus occurrence of
50 matches.
The journals’ geographic origins were identified from
PubMed records, and the first author’s geographic origin
was obtained from their reported affiliation. The main
Figure 1. Workflow diagram illustrating the selection process of clinical diagnosis was obtained from PubMed’s Medical Subject
case reports. The figure was created with yEd. Headings (MeSH) codes corresponding to disease or
Abbreviations: BERT: Bidirectional Encoder Representations from
Transformers for Biomedical Text Mining; NER: Named-entity mental condition categories. Only root primary disease
recognition; SDoH: Social determinants of health; XML: Extensible categories (e.g., respiratory tract, neurological, and mental
markup language. conditions) were used during the analysis.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 119 doi: 10.36922/aih.2737