Page 43 - AIH-1-2
P. 43
Artificial Intelligence in Health Blockchain for health-care security
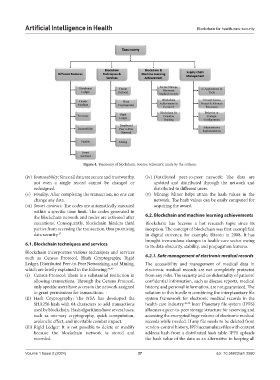
Figure 4. Taxonomy of blockchain. Source: Schematic made by the authors.
(iv) Immutability: Since all data are secure and trustworthy, (iv) Distributed peer-to-peer network: The data are
not even a single record cannot be changed or updated and distributed through the network and
redesigned. distributed to different users.
(v) Finality: After completing the transaction, no one can (v) Mining: Miner helps attain the hash values in the
change any data. network. The hash values can be easily computed for
(vi) Smart contract: The codes are automatically executed acquiring the award.
within a specific time limit. The codes generated in
the blockchain network and nodes are activated after 6.2. Blockchain and machine learning achievements
executions. Consequently, blockchain hinders third Blockchain has become a hot research topic since its
parties from accessing the transaction, thus promising inception. The concept of blockchain was first exemplified
data security. 17 in digital currency, for example, Bitcoin in 2008. It has
brought tremendous changes in health-care sector owing
6.1. Blockchain techniques and services to its data obscurity, stability, and propagation features.
Blockchain incorporates various techniques and services
such as Census Protocol, Hash Cryptography, Rigid 6.2.1. Safe management of electronic medical records
Ledger, Distributed Peer-to-Peer Networking, and Mining, The accessibility and management of medical data in
which are briefly explained in the following: 45,49 electronic medical records are not completely protected
(i) Census Protocol: There is a substantial restriction in from any risks. The security and confidentiality of patients’
allowing transactions. Through the Census Protocol, confidential information, such as disease reports, medical
only specific users have access to the network assigned history, and personal information, are not guaranteed. The
to grant permissions for transactions. solution to this hurdle is combining the interplanetary file
(ii) Hash Cryptography: The NSA has developed the system framework for electronic medical records in the
SHA256 hash with 64 characters to add transactions health-care industry. 40,50 Inter Planetary file system (IPFS)
used by blockchain. Hash algorithms have several uses, allocates a peer-to-peer storage structure for reserving and
such as one-way cryptography, quick computation, accessing the encrypted huge volume of electronic medical
avalanche effect, and inevitable combat impact. records while needed. If any file needs to be deleted from
(iii) Rigid Ledger: It is not possible to delete or modify version-control history, IPFS accumulates files with content
because the blockchain network is stored and address hash from a distributed hash table. IPFS uploads
recorded. the hash value of the data as an alternative to keeping all
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 37 doi: 10.36922/aih.2580