Page 40 - AIH-1-2
P. 40
Artificial Intelligence in Health Blockchain for health-care security
of the PBFT algorithm is significantly different because the
blockchain nodes are shared and maintained by multiple
nodes, complicating the process of detecting medical data
and protecting them from potential attackers. 29
In general, the performance of these algorithms directly
affects the utilization of medical data systems based on
blockchain frameworks. However, depending on the
kind of health-care application, the time delay during
these algorithms processing will negatively impact the
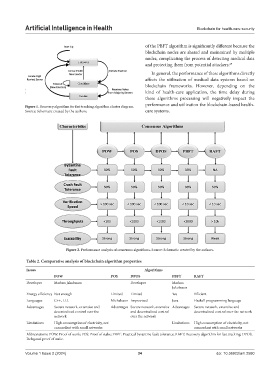
Figure 1. Recovery algorithm for fast tracking algorithm cluster diagram. performance and utilization the blockchain-based health-
Source: Schematic created by the authors. care systems.
Figure 2. Performance analysis of consensus algorithms. Source: Schematic created by the authors.
Table 2. Comparative analysis of blockchain algorithm properties
Issues Algorithms
POW POS DPOS PBFT RAFT
Developer Markus Jakobsson Developer Markus
Jakobsson
Energy efficiency Not enough Limited Limited Yes Efficient
Languages C++, LLL Michaleson Improvised Java Haskell programming language
Advantages Secure network, extensive and Advantages Secure network, extensive Advantages Secure network, extensive and
decentralized control over the and decentralized control decentralized control over the network
network over the network
Limitations High consumption of electricity, not Limitations High consumption of electricity, not
concordant with small networks concordant with small networks
Abbreviations: POW: Proof of work; POS: Proof of stake; PBFT: Practical byzantine fault tolerance; RAFT: Recovery algorithm for fast tracking; DPOS:
Delegated proof of stake.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 34 doi: 10.36922/aih.2580