Page 45 - AIH-1-2
P. 45
Artificial Intelligence in Health Blockchain for health-care security
Table 5. List of the characteristics of blockchain technology and their descriptions
Characteristics Description
Decentralization • Blockchain technology is a serialized data structure used to establish a decentralized ledger.
• Decentralization allows parties to transact data in the health-care sector without involving a third party, reducing financial bias and fraud.
Trustlessness Payments are made only when the balance is available on the blockchain, a feature that is essential to secure financial balances.
User-centricity • The user-centricity attribute of blockchain technology ensures patients in control of their personal financial data.
• Blockchain allows the patient to become the key mediator in distributing his or her medical data.
• Patient or family member must expressly grant the provider access to the patient’s medical record governed by the patient’s private
key signature for every new medical interaction.
• Every access to patient’s data is recorded in the immutable transaction history of the blockchain, providing a clear record of who has
accessed and edited the patient’s record.
Transparency • Every transaction data in the blockchain is publicly viewable.
Immutability • Blockchain is impervious to data manipulation.
• The immutability of the blockchain ledger means that transactions cannot be changed or removed once they have been recorded.
• Blockchains serve as a data timekeeping system, allowing easy data history reporting.
Speed • Blockchain technology helps enhance the efficiency of verification for health‑care sector transactions between financial institutions.
Cost • Blockchain technology obviates the need to pay transaction fees by removing intermediaries from the health‑care transaction.
applications. 18,44 There are other applications that have used
blockchain technology in the field of health care, which are
explained in the following subsections.
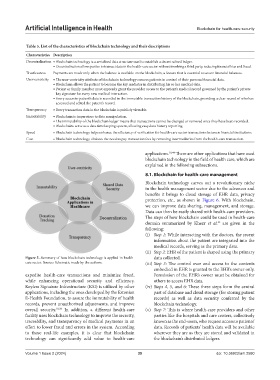
8.1. Blockchain for health-care management
Blockchain technology carves out a revolutionary niche
in the health management sector due to the advances and
benefits it brings to cloud storage of EHR data, privacy
protection, etc., as shown in Figure 6. With blockchain,
we can improve data sharing, management, and storage.
Data can then be easily shared with health-care providers.
The steps of how blockchain could be used in health-care
32
domain summarized by Khezr et al. are given in the
following:
(i) Step 1: While interacting with the doctors, the recent
information about the patient are integrated into the
medical records, serving as the primary data.
(ii) Step 2: EHR of the patient is shaped using the primary
Figure 5. Summary of how blockchain technology is applied in health- data collected.
care sector. Source: Schematic made by the authors. (iii) Step 3: The control over and access to the contents
embodied in EHR is granted to the EHR’s owner only.
expedite health-care transactions and minimize fraud, Permission of the EHR’s owner must be obtained for
while enhancing operational security and efficiency. others to access EHR data.
Keyless Signature Infrastructure (KSI) is utilized by other (iv) Steps 4, 5, and 6: These three steps form the central
applications, including the ones developed by the Estonian part of database and cloud storage (for storing patient
E-Health Foundation, to assure the immutability of health records) as well as data security conferred by the
records, prevent unauthorized adjustments, and improve blockchain technology.
overall security. 18,36 In addition, a different health-care (v) Step 7: This is where health-care providers and other
facility uses blockchain technology to improve the security, parties like the hospitals and care centers, collectively
traceability, and transparency of medical payments in an known as the end-users, who request access to patients’
effort to lower fraud and errors in the system. According data. Records of patients’ health data will be available
to these real-life examples, it is clear that blockchain wherever they are as they are stored and validated in
technology can significantly add value to health-care the blockchain’s distributed ledgers.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 39 doi: 10.36922/aih.2580