Page 38 - AIH-1-2
P. 38
Artificial Intelligence in Health Blockchain for health-care security
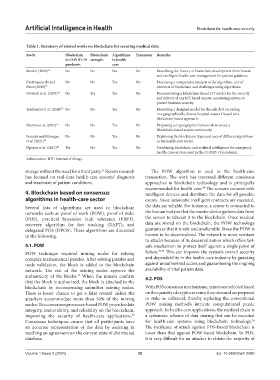
Table 1. Summary of related works on blockchain for securing medical data
Study Blockchain Blockchain Algorithms Taxonomy Remarks
in COVID‑19 strength in health
pandemic care
Mettler (2016) 14 No No No No Describing the history of blockchain development from bitcoin
and intelligent health-care management for patient guidance.
Krishnamurthi and No No Yes No Presenting a comparative analysis of the algorithm, a brief
Shree (2019) 15 overview of blockchain and challenges using algorithms.
Dwivedi et al. (2019) 16 No Yes Yes No Demonstrating a blockchain-based IoT model for the security
and privacy of any IoT-based remote monitoring system to
protect business security.
Yazdinejad et al. (2020) 17 No No Yes No Presenting a designed model for the safe data recording
in a geographically diverse hospital network based on a
blockchain-based approach.
Sharma et al. (2021) 18 No No Yes No Proposing a cryptographic framework to create a
blockchain-based secure community.
Saranya and Murugan No No Yes No Explaining the blockchain types and uses of different algorithms
et al. (2021) 19 in the health-care sector.
Nguyen et al. (2021) 20 Yes No Yes No Combining blockchain and artificial intelligence for emergency
health-care services used in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Abbreviation: IOT: Internet of things.
storage without the need for a third party. Recent research The POW algorithm is used in the health-care
31
has focused on real-time health-care systems’ diagnosis transaction. The work has traversed different consensus
and treatment of patient conditions. approaches in blockchain technology and is principally
recommended for health care. The sensors connect with
34
4. Blockchain based on consensus intelligent devices and distribute the data for all possible
algorithms in health-care sector events. Since automatic intelligent contracts are executed,
Several lists of algorithms are used in blockchain the data are reliable. For instance, a sensor is connected to
networks such as proof of work (POW), proof of stake the human body so that the master device gathers data from
(POS), practical byzantine fault tolerance (PBFT), the sensor to telecast it to the blockchain. Once medical
recovery algorithm for fast tracking (RAFT), and data are stored on the blockchain, the POW technology
delegated POS (DPOS). These algorithms are discussed guarantees that it is safe and unalterable. Since the POW is
in the following. known to be decentralized. The network is more resistant
to attacks because of its decentralization which offers fail-
4.1. POW safe mechanism to protect itself against a single point of
POW technique required mining nodes for solving failure. 29,35 This can improve the system’s overall security
complex mathematical puzzles. After solving puzzles and and dependability in the health-care industry by guarding
node validation, the block is added to the blockchain against unauthorized access and guaranteeing the ongoing
network. The rest of the mining nodes approve the availability of vital patient data.
authenticity of the blocks. When the miners confirm 4.2. POS
32
that the block is authorized, the block is attached to the
blockchain by recompensing submitter mining nodes. With POS consensus mechanisms, miners are selected based
There is lesser chance to get a false reward unless the on the quantity of cryptocurrency they own and are prepared
attackers accommodate more than 50% of the mining to stake as collateral, thereby replacing the conventional
nodes. The consensus processes-based POW provides data POW mining method’s intricate computational puzzle
integrity, immutability, and reliability on the blockchain, approach. In health-care applications, the medical chain is
improving the security of health-care applications. a systematic scheme of data sharing that can be executed
33
34
Consensus techniques ensure that all participants have for health-care systems using blockchain technology.
an accurate representation of the data by assisting in The incidence of attack against POS-based blockchain is
reaching an agreement on the current state of distributed lesser than that against POW-based blockchain. In POS,
database. it is very difficult for an attacker to obtain the majority of
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 32 doi: 10.36922/aih.2580