Page 43 - AIH-1-3
P. 43
Artificial Intelligence in Health Predicting mortality in COVID-19 using ML
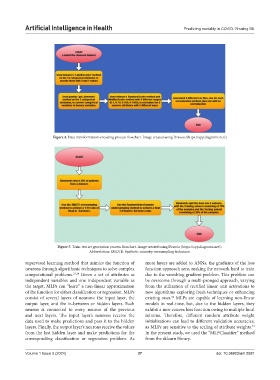
Figure 4. Data transformation-encoding process flowchart. Image created using Draw.io (https://app.diagrams.net/)
Figure 5. Train-test set generation process flowchart. Image created using Draw.io (https://app.diagrams.net/).
Abbreviation: SMOTE: Synthetic minority oversampling technique.
supervised learning method that mimics the function of more layers are added to ANNs, the gradients of the loss
neurons through algorithmic techniques to solve complex function approach zero, making the network hard to train
computational problems. 33,34 Given a set of attributes as due to the vanishing gradient problem. This problem can
independent variables and one independent variable as be overcome through a multi-pronged approach, varying
the target, MLPs can “learn” a non-linear approximation from the utilization of rectified linear unit activations to
of the function for either classification or regression. MLPs new algorithms exploring fresh techniques or enhancing
consist of several layers of neurons: the input layer, the existing ones. MLPs are capable of learning non-linear
52
output layer, and the in-between or hidden layers. Each models in real-time, but, due to the hidden layers, they
neuron is connected to every neuron of the previous exhibit a non-convex loss function owing to multiple local
and next layers. The input layer’s neurons receive the minima. Therefore, different random attribute weight
data used to make predictions and pass it to the hidden initializations can lead to different validation accuracies,
layers. Finally, the output layer’s neurons receive the values as MLPs are sensitive to the scaling of attribute weights.
53
from the last hidden layer and make predictions for the In the present study, we used the “MLPClassifier” method
corresponding classification or regression problem. As from the sklearn library.
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 37 doi: 10.36922/aih.2591