Page 47 - AIH-1-3
P. 47
Artificial Intelligence in Health Predicting mortality in COVID-19 using ML
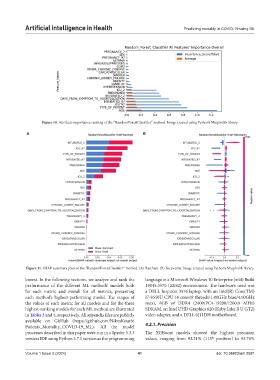
Figure 10. Attribute importance ranking of the “RandomForestClassifier” method. Image created using Python’s Matplotlib library
A B
Figure 11. SHAP summary plots of the “RandomForestClassifier” method. (A) Barchart. (B) Beeswarm. Image created using Python’s Matplotlib library
lowest. In the following sections, we analyze and rank the language in a Microsoft Windows 10 Enterprise (x64) Build
performance of the different ML methods’ models both 19045.3570 (22H2) environment. The hardware used was
for each metric and overall for all metrics, presenting a DELL Inspiron 3576 laptop, with an Intel(R) Core(TM)
each method’s highest-performing model. The ranges of i7-8550U CPU (4 cores/8 threads/1.80GHz base/4.00GHz
the values of each metric for all models and for the three max), 8GB of DDR4 (2400/PC4-19200/1200.0 MHz)
highest-ranking models for each ML method are illustrated SDRAM, an Intel UHD Graphics 620 (Kaby Lake R U GT2)
in Tables 3 and 4, respectively. All appendix files are publicly video adapter, and a DELL 0J11DH motherboard.
available on GitHub (https://github.com/NikosKourb/
Patients_Mortality_COVID-19_ML). All the model 4.2.1. Precision
processes described in this paper were run in a Spyder 5.3.3 The XGBoost models showed the highest precision
version IDE using Python 3.7.1 version as the programming values, ranging from 93.21% (113 position) to 93.76%
th
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 41 doi: 10.36922/aih.2591