Page 62 - AIH-1-3
P. 62
Artificial Intelligence in Health ChatGPT in writing scientific articles
publishing journal names. These are real sources that 3.2. Comparison of source reliability for generated
can theoretically be used in the preparation of an articles
article on the specified topics. The total number of sources used for generating scientific
(ii) Semi-reliable sources (“red”): These sources have a articles on the topic of biotelemetry in cardiology was
real title of the article but incorrect publication year, 260 (155 for ChatGPT 3.5 and 105 for ChatGPT 4).
journal, and/or authors’ names. The “red” group also For articles generated on the topic of biotelemetry in
included Internet sources (websites of biomedical oncology, the neural network produced 269 sources (157
companies, Wikipedia, and others). Such online for ChatGPT 3.5 and 112 for ChatGPT 4). For articles on
sources were actively cited by ChatGPT 4 when it was the topic of biotelemetry in remote medical examination,
unable to find other journal publications. It is worth 246 (150 for ChatGPT 3.5 and 96 for ChatGPT 4) sources
noting that all the “red” sources for this version turned
out to be Internet sources. were obtained.
(iii) Fictitious sources (“yellow”): These sources have a Source verification was carried out. Figure 2 shows the
completely fictitious title, authors, and sometimes a normalized distribution charts of the reliability of literature
fictitious journal name. sources according to the source classification described
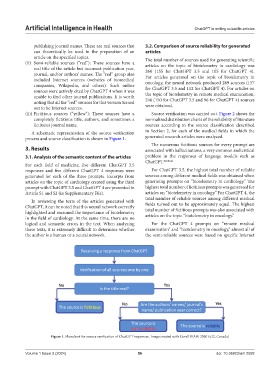
A schematic representation of the source verification in Section 2, for each of the medical fields in which the
process and source classification is shown in Figure 1. generated research articles were analyzed.
The numerous fictitious sources for every prompt are
3. Results associated with hallucinations, a very common and critical
3.1. Analysis of the semantic content of the articles problem in the responses of language models such as
ChatGPT. 28,40,41
For each field of medicine, five different ChatGPT 3.5
responses and five different ChatGPT 4 responses were For ChatGPT 3.5, the highest total number of reliable
generated for each of the three prompts. Excerpts from sources among different medical fields was obtained when
articles on the topic of cardiology created using the third generating prompts on “biotelemetry in cardiology.” The
prompt with ChatGPT 3.5 and ChatGPT 4 are presented in highest total number of fictitious prompts was generated for
Article S1 and S2 (in Supplementary File). articles on “biotelemetry in oncology.” For ChatGPT 4, the
total number of reliable sources among different medical
In reviewing the texts of the articles generated with
ChatGPT, it can be noted that this neural network correctly fields turned out to be approximately equal. The highest
total number of fictitious prompts was also associated with
highlighted and reasoned the importance of biotelemetry articles on the topic “biotelemetry in oncology.”
in the field of cardiology. At the same time, there are no
logical and semantic errors in the text. When analyzing For the ChatGPT 4 prompts on “remote medical
these texts, it is extremely difficult to determine whether examination” and “biotelemetry in oncology,” almost all of
the author is a human or a neural network. the semi-reliable sources were based on specific Internet
Figure 1. Flowchart for source verification of ChatGPT responses. Image created with CorelDRAW 2020 (v22, Canada)
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 56 doi: 10.36922/aih.2592