Page 39 - AIH-2-1
P. 39
Artificial Intelligence in Health Deep learning on chest X-ray and CT for COVID-19
Figure 1. Sample images are taken from the dataset. 34,35,37 The indication above each image corresponds to the associated label. Image created by the author.
sketch their outlines, although complete details can be A B
found in the reference mentioned in the corresponding
sections. Fundamental building blocks are schematically
depicted in Figure 2A-D.
2.2.1. Method 1: ResNet34
Developing a proper training protocol is a matter of
serious concern for the implementation of any deep neural
network. One such major issue is the divergence from local
minima, leading to improper training. To address this, in C D
ResNet, a modification in the network architecture was
38
introduced by incorporating skip connections, expressed
as H(x) + x, between layers. This alteration facilitated
quicker and more efficient model training. The smooth loss
landscape of ResNet prevents the model from becoming
trapped in local minima or saddle points, resulting in
improved training speed and accuracy. In our study,
we utilized a variant of ResNet, specifically ResNet34,
consisting of a total of 34 convolutional layers.
2.2.2. Method 2: SeResNext50
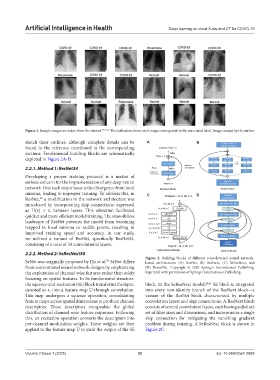
Figure 2. Building blocks of different convolutional neural network-
SeNet was originally proposed by Hu et al. SeNet differs based architectures: (A) ResNet, (B) ResNext, (C) SeResNext, and
39
from conventional neural network designs by emphasizing (D) DenseNet. Copyright © 2020 Springer International Publishing.
the exploration of channel-wise features rather than solely Reprinted with permission of Springer International Publishing.
focusing on spatial features. In its fundamental structure,
the squeeze-and-excitation (SE) block transforms the input, block. In the SeResNext model, 40,41 SE block is integrated
denoted as x, into a feature map U through convolution. into every non-identity branch of the ResNext block—a
This map undergoes a squeeze operation, consolidating variant of the ResNet block characterized by multiple
feature maps across spatial dimensions to produce channel convolution layers and skip connections. A ResNext block
descriptors. These descriptors encapsulate the global consists of several convolution layers, each having a distinct
distribution of channel-wise feature responses. Following set of filter sizes and dimensions, and incorporates a single
this, an excitation operation converts the descriptors into skip connection for mitigating the vanishing gradient
per-channel modulation weights. These weights are then problem during training. A SeResNext block is shown in
applied to the feature map U to yield the output of the SE Figure 2C.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 33 doi: 10.36922/aih.2888