Page 43 - AIH-2-1
P. 43
Artificial Intelligence in Health Deep learning on chest X-ray and CT for COVID-19
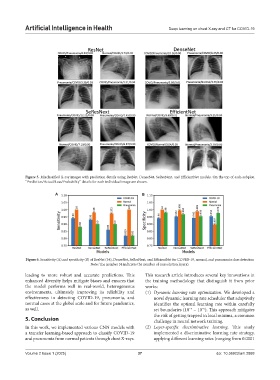
Figure 5. Misclassified X-ray images with prediction details using ResNet, DenseNet, SeResNext, and EfficientNet models. On the top of each subplot,
“Prediction/Actual/Loss/Probability” details for each individual image are shown.
A B
Figure 6. Sensitivity (A) and specificity (B) of ResNet (34), DenseNet, SeResNext, and EfficientNet for COVID-19, normal, and pneumonia class detection
Note: The number 34 indicates the number of convolution layers).
leading to more robust and accurate predictions. This This research article introduces several key innovations in
enhanced diversity helps mitigate biases and ensures that the training methodology that distinguish it from prior
the model performs well in real-world, heterogeneous works:
environments, ultimately improving its reliability and (1) Dynamic learning rate optimization. We developed a
effectiveness in detecting COVID-19, pneumonia, and novel dynamic learning rate scheduler that adaptively
normal cases at the global scale and for future pandemics, identifies the optimal learning rate within carefully
as well. set boundaries (10 – 10 ). This approach mitigates
−4
−5
the risk of getting trapped in local minima, a common
5. Conclusion challenge in neural network training.
In this work, we implemented various CNN models with (2) Layer-specific discriminative learning. This study
a transfer learning-based approach to classify COVID-19 implemented a discriminative learning rate strategy,
and pneumonia from normal patients through chest X-rays. applying different learning rates (ranging from 0.0001
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 37 doi: 10.36922/aih.2888