Page 52 - AIH-2-1
P. 52
Artificial Intelligence in Health Asymmetric U-Net for enhanced spinal MRI segmentation
internal information flow and integration within the In the J-Unet model, each decoder layer is connected
network, improves the perception of detailed structures and to the largest-scale feature map from the most adjacent
edges, and ultimately boosts the accuracy of segmentation layer through a residual connection, allowing for the
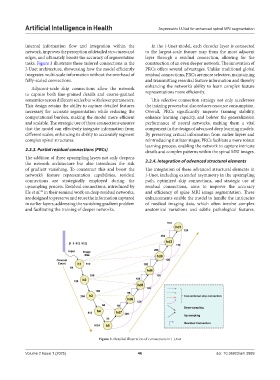
tasks. Figure 3 illustrates these tailored connections in the construction of an even deeper network. The innovation of
J-Unet architecture, showcasing how the model efficiently PRCs offers several advantages. Unlike traditional global
integrates multi-scale information without the overhead of residual connections, PRCs are more selective, maintaining
fully-scaled connections. and transmitting essential feature information and thereby
Adjacent-scale skip connections allow the network enhancing the network’s ability to learn complex feature
to capture both fine-grained details and coarse-grained representations more efficiently.
semantics across different scales but with fewer parameters. This selective connection strategy not only accelerates
This design retains the ability to capture detailed features the training process but also reduces resource consumption.
necessary for accurate segmentation while reducing the Overall, PRCs significantly improve training stability,
computational burden, making the model more efficient enhance learning capacity, and bolster the generalization
and scalable. The strategic use of these connections ensures performance of neural networks, making them a vital
that the model can effectively integrate information from component in the design of advanced deep learning models.
different scales, enhancing its ability to accurately segment By preserving critical information from earlier layers and
complex spinal structures. reintroducing it at later stages, PRCs facilitate a more robust
learning process, enabling the network to capture intricate
2.2.3. Partial residual connections (PRCs) details and complex patterns within the spinal MRI images.
The addition of three upsampling layers not only deepens
the network architecture but also introduces the risk 2.2.4. Integration of advanced structural elements
of gradient vanishing. To counteract this and boost the The integration of these advanced structural elements in
network’s feature representation capabilities, residual J-Unet, including extended asymmetry in the upsampling
connections are strategically employed during the path, optimized skip connections, and strategic use of
upsampling process. Residual connections, introduced by residual connections, aims to improve the accuracy
He et al. in their seminal work on deep residual networks, and efficiency of spine MRI image segmentation. These
30
are designed to preserve and reuse the information captured enhancements enable the model to handle the intricacies
in earlier layers, addressing the vanishing gradient problem of medical imaging data, which often involve complex
and facilitating the training of deeper networks. anatomical variations and subtle pathological features.
Figure 3. Detailed illustration of connections in J-Unet
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 46 doi: 10.36922/aih.3889