Page 55 - AIH-2-1
P. 55
Artificial Intelligence in Health Asymmetric U-Net for enhanced spinal MRI segmentation
A B
C D
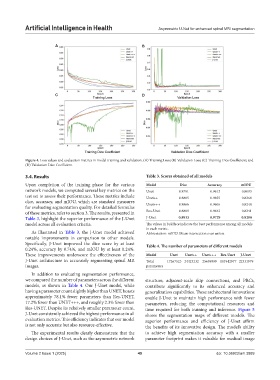
Figure 4. Loss values and evaluation metrics in model training and validation. (A) Training Loss; (B) Validation Loss; (C) Training Dice Coefficient; and
(D) Validation Dice Coefficient
3.4. Results Table 3. Scores obtained of all models
Upon completion of the training phase for the various Model Dice Accuracy mIOU
network models, we computed several key metrics on the Unet 0.8791 0.9613 0.8093
test set to assess their performance. These metrics include Unet++ 0.8885 0.9655 0.8264
dice, accuracy, and mIOU, which are standard measures Unet+++ 0.8866 0.9606 0.8248
for evaluating segmentation quality. For detailed formulas
of these metrics, refer to section 3. The results, presented in Res-Unet 0.8889 0.9642 0.8241
Table 3, highlight the superior performance of the J-Unet J-Unet 0.8913 0.9729 0.8288
model across all evaluation criteria. The values in boldface indicate the best performance among all models
in each metric.
As illustrated in Table 3, the J-Unet model achieved Abbreviation: mIOU: Mean intersection over union.
notable improvements in comparison to other models.
Specifically, J-Unet improved the dice score by at least Table 4. The number of parameters of different models
0.24%, accuracy by 0.74%, and mIOU by at least 0.24%.
These improvements underscore the effectiveness of the Model Unet Unet++ Unet+++ Res‑Unet J‑Unet
J-Unet architecture in accurately segmenting spinal MR Total 17267523 24423232 25659999 101942977 22331979
images. parameters
In addition to evaluating segmentation performance,
we compared the number of parameters across the different structure, adjacent-scale skip connections, and PRCs,
models, as shown in Table 4. Our J-Unet model, while contribute significantly to its enhanced accuracy and
having a parameter count slightly higher than UNET, boasts generalization capabilities. These architectural innovations
approximately 78.1% fewer parameters than Res-UNET, enable J-Unet to maintain high performance with fewer
17.2% fewer than UNET+++, and roughly 2.3% fewer than parameters, reducing the computational resources and
Res-UNET. Despite its relatively smaller parameter count, time required for both training and inference. Figure 5
J-Unet consistently achieved the highest performance in all shows the segmentation maps of different models. The
evaluation metrics. This efficiency indicates that our model superior performance and efficiency of J-Unet affirm
is not only accurate but also resource-effective. the benefits of its innovative design. The model’s ability
The experimental results clearly demonstrate that the to achieve high segmentation accuracy with a smaller
design choices of J-Unet, such as the asymmetric network parameter footprint makes it valuable for medical image
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 49 doi: 10.36922/aih.3889