Page 78 - AIH-2-1
P. 78
Artificial Intelligence in Health ViT for Glioma Classification in MRI
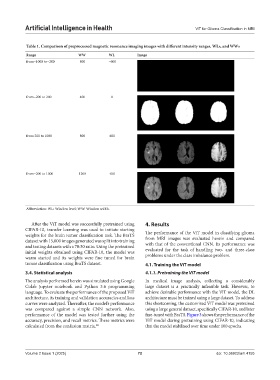
Table 1. Comparison of preprocessed magnetic resonance imaging images with different intensity ranges, WLs, and WWs
Range WW WL Image
from−1000 to−200 800 −600
from−200 to 200 400 0
from 200 to 1000 800 600
from−200 to 1000 1200 400
Abbreviation: WL: Window level; WW: Window width.
After the ViT model was successfully pretrained using 4. Results
CIFAR-10, transfer learning was used to initiate starting
weights for the brain tumor classification task. The BraTS The performance of the ViT model in classifying glioma
dataset with 15,000 images generated was split into training from MRI images was evaluated herein and compared
and testing datasets with a 70:30 ratio. Using the pretrained with that of the conventional CNN. Its performance was
initial weights obtained using CIFAR-10, the model was evaluated for the task of handling two- and three-class
warm started and its weights were fine tuned for brain problems under the class imbalance problem.
tumor classification using BraTS dataset. 4.1. Training the ViT model
3.4. Statistical analysis 4.1.1. Pretraining the ViT model
The analysis performed herein was simulated using Google In medical image analysis, collecting a considerably
Colab Jupyter notebook and Python 3.6 programming large dataset is a practically infeasible task. However, to
language. To evaluate the performance of the proposed ViT achieve desirable performance with the ViT model, the DL
architecture, its training and validation accuracies and loss architecture must be trained using a large dataset. To address
curves were analyzed. Thereafter, the model’s performance this shortcoming, the customized ViT model was pretrained
was compared against a simple CNN network. Also, using a large general dataset, specifically CIFAR-10, and later
performance of the model was tested further using the fine-tuned with BraTS. Figure 3 shows the performance of the
accuracy, precision, and recall metrics. These metrics were ViT model during pretraining using CIFAR-10, indicating
calculated from the confusion matrix. 28 that the model stabilized over time under 100 epochs.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 72 doi: 10.36922/aih.4155