Page 82 - AIH-2-1
P. 82
Artificial Intelligence in Health ViT for Glioma Classification in MRI
A B
C
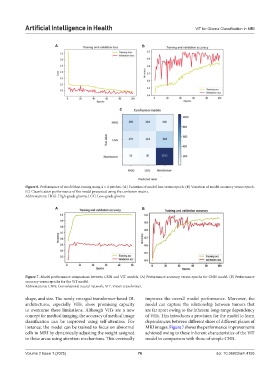
Figure 6. Performance of model fine-tuning using 4 × 4 patches. (A) Variation of model loss versus epoch. (B) Variation of model accuracy versus epoch.
(C) Classification performance of the model presented using the confusion matrix.
Abbreviations: HGG: High-grade glioma; LGG: Low-grade glioma
A B
Figure 7. Model performance comparison between CNN and ViT models. (A) Performance accuracy versus epochs for CNN model. (B) Performance
accuracy versus epochs for the ViT model.
Abbreviations: CNN: Convolutional neural network; ViT: Vision transformer.
shape, and size. The newly emerged transformer-based DL improves the overall model performance. Moreover, the
architectures, especially ViTs, show promising capacity model can capture the relationship between tumors that
to overcome these limitations. Although ViTs are a new are far apart owing to the inherent long-range dependency
concept for medical imaging, the accuracy of medical image of ViTs. This introduces a provision for the model to learn
classification can be improved using self-attention. For dependencies between different slices of different planes of
instance, the model can be trained to focus on abnormal MRI images. Figure 7 shows the performance improvements
cells in MRI by dynamically adjusting the weight assigned achieved owing to these inherent characteristics of the ViT
to these areas using attention mechanisms. This eventually model in comparison with those of simple CNN.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 76 doi: 10.36922/aih.4155